Cooling in the rock cycle
Home » Science Education » Cooling in the rock cycleCooling in the rock cycle
Cooling In The Rock Cycle. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Cooling of igneous rocks can occur slowly beneath the surface of the earth or rapidly at its surface. Igneous rocks are the result of cooling and crystallizing magma. Melting is the first then cooling and crystallization followed by weathering and erosion and deportation next comes cementation and compaction and.
 A Wild Ride Through The Rock Cycle Use Natural Stone From usenaturalstone.org
A Wild Ride Through The Rock Cycle Use Natural Stone From usenaturalstone.org
When magma cools and forms into solid rock there are two different processes involved. Igneous crystals are formed when freely moving atoms in melted rock become arranged in orderly patterns as they cool. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other existing rock or organic material. Melting is the first then cooling and crystallization followed by weathering and erosion and deportation next comes cementation and compaction and. Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface.
As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure.
Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. Steps of the rock cycle 1 formation of igneous rock melting cooling and crystallization magma the molten rock present deep inside the earth solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks. When heated deep under ground rocks become magma liquid rock. When magma cools and forms into solid rock there are two different processes involved. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Each of these rocks can change into the other kinds by physical processes.
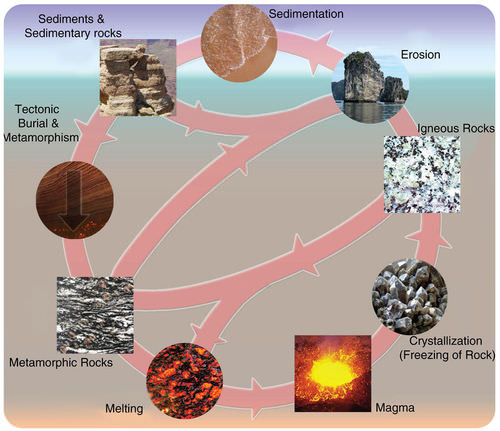
One other process in the rock cycle is the cooling phase which occurs when rocks are taken out of the high heat and pressure environments that caused change. Cooling melting heat weathering erosion compacting squeezing tightly together cementing and pressure. One other process in the rock cycle is the cooling phase which occurs when rocks are taken out of the high heat and pressure environments that caused change. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes such as melting cooling eroding compacting or deforming that are part of the rock cycle. Sedimentary igneous and metamorphic.
 Source: learning-center.homesciencetools.com
Source: learning-center.homesciencetools.com
Above ground it is called lava. Cooling of igneous rocks can occur slowly beneath the surface of the earth or rapidly at its surface. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Above ground it is called lava. Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava.
 Source: academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu
Source: academic.brooklyn.cuny.edu
Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other existing rock or organic material. When magma cools and forms into solid rock there are two different processes involved. Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. One other process in the rock cycle is the cooling phase which occurs when rocks are taken out of the high heat and pressure environments that caused change.
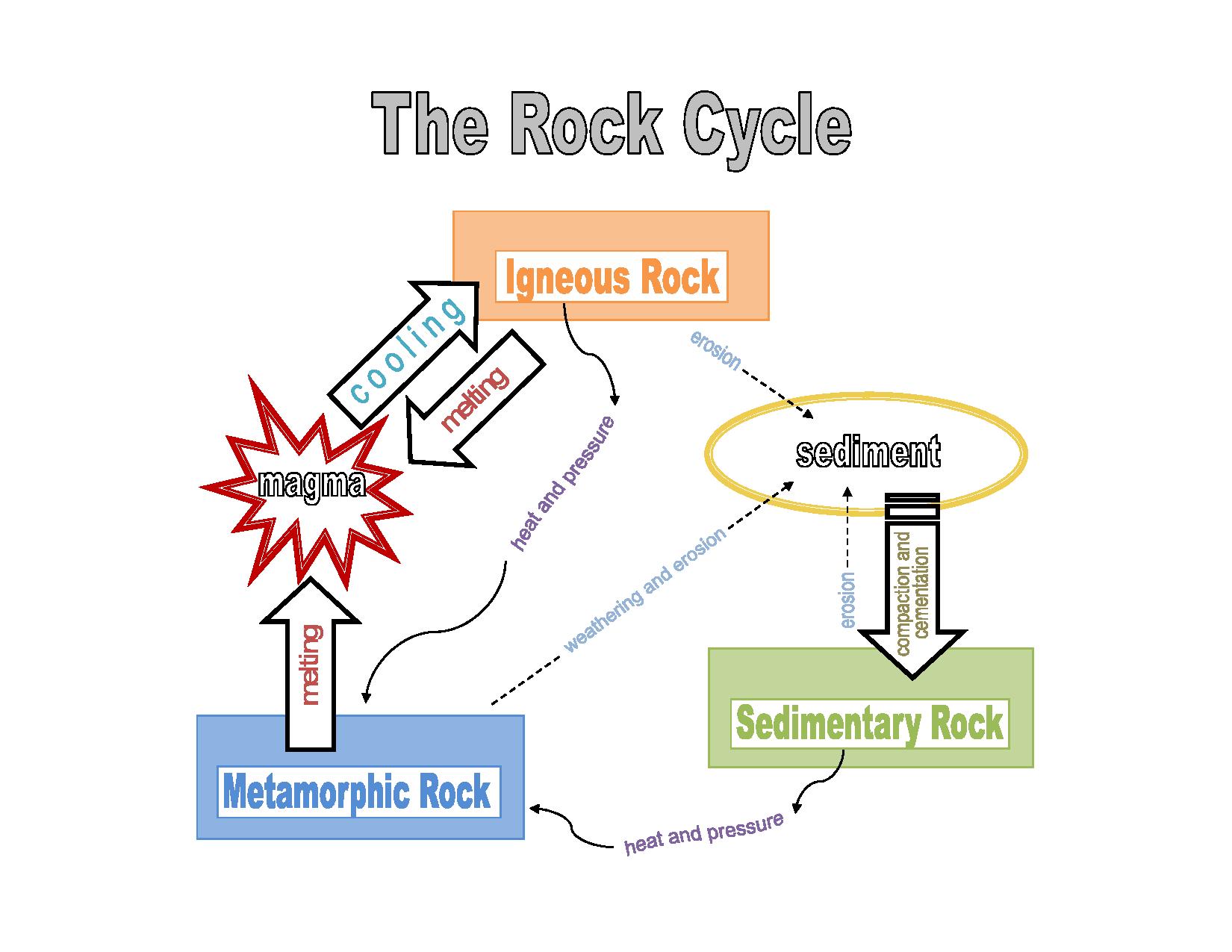
 Source: cotf.edu
Source: cotf.edu
The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Igneous rocks are the result of cooling and crystallizing magma. As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure. Above ground it is called lava. Igneous crystals are formed when freely moving atoms in melted rock become arranged in orderly patterns as they cool.
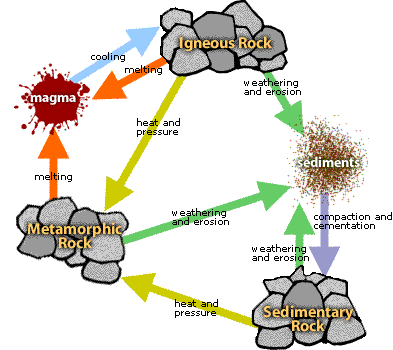
 Source: physicalgeography.net
Source: physicalgeography.net
One other process in the rock cycle is the cooling phase which occurs when rocks are taken out of the high heat and pressure environments that caused change. Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. Quickly cooling rock often extrusive lava that comes from volcanoes or fissures in the earth s surface has small crystals and may be quite smooth such as the volcanic obsidian rock. Cooling melting heat weathering erosion compacting squeezing tightly together cementing and pressure. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes such as melting cooling eroding compacting or deforming that are part of the rock cycle.
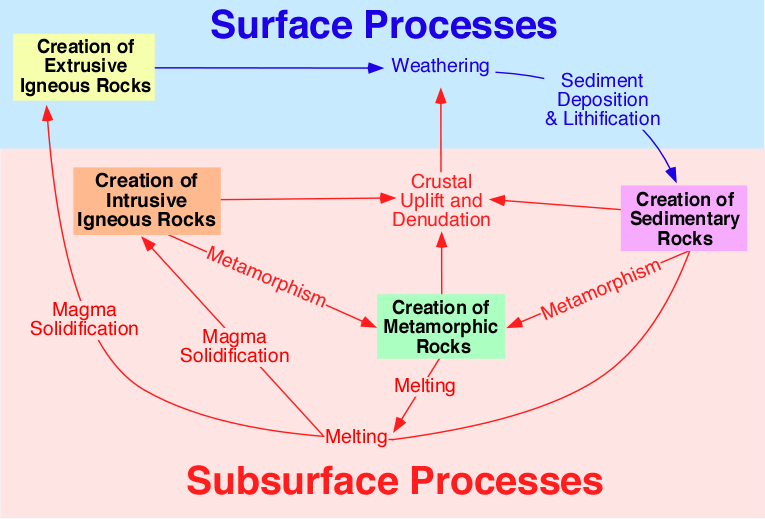
 Source: rocksandminerals.com
Source: rocksandminerals.com
Igneous rocks are the result of cooling and crystallizing magma. Above ground it is called lava. The magma that forms igneous rock beneath the surface of the earth can take thousands of years to cool. As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure. There are five sequences in the rock cycle.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface. Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava. Cooling of igneous rocks can occur slowly beneath the surface of the earth or rapidly at its surface. The magma that forms igneous rock beneath the surface of the earth can take thousands of years to cool. When magma cools and forms into solid rock there are two different processes involved.
 Source: clarkscience8.weebly.com
Source: clarkscience8.weebly.com
When heated deep under ground rocks become magma liquid rock. Igneous crystals are formed when freely moving atoms in melted rock become arranged in orderly patterns as they cool. There are three main types of rocks. The magma that forms igneous rock beneath the surface of the earth can take thousands of years to cool. Quickly cooling rock often extrusive lava that comes from volcanoes or fissures in the earth s surface has small crystals and may be quite smooth such as the volcanic obsidian rock.
 Source: sfcollege.edu
Source: sfcollege.edu
As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure. Quickly cooling rock often extrusive lava that comes from volcanoes or fissures in the earth s surface has small crystals and may be quite smooth such as the volcanic obsidian rock. Steps of the rock cycle 1 formation of igneous rock melting cooling and crystallization magma the molten rock present deep inside the earth solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks. Igneous crystals are formed when freely moving atoms in melted rock become arranged in orderly patterns as they cool. One other process in the rock cycle is the cooling phase which occurs when rocks are taken out of the high heat and pressure environments that caused change.
 Source: usenaturalstone.org
Source: usenaturalstone.org
Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Each of these rocks can change into the other kinds by physical processes. Above ground it is called lava. Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava.
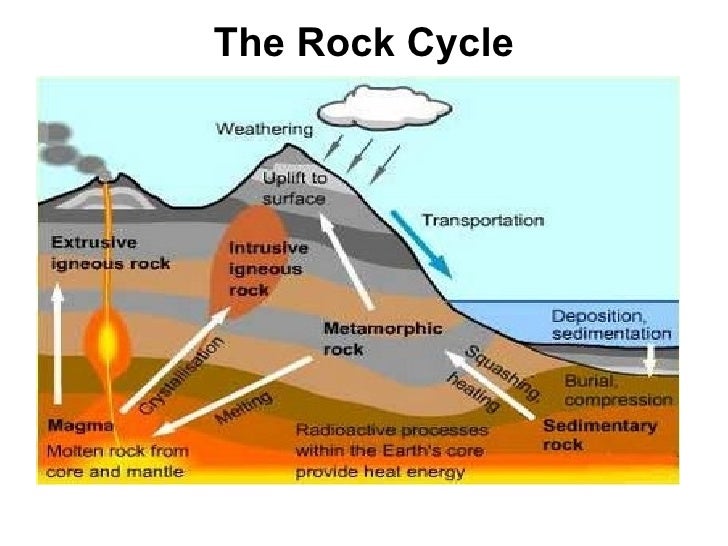 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust. Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes such as melting cooling eroding compacting or deforming that are part of the rock cycle. Steps of the rock cycle 1 formation of igneous rock melting cooling and crystallization magma the molten rock present deep inside the earth solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks. When heated deep under ground rocks become magma liquid rock. The magma that forms igneous rock beneath the surface of the earth can take thousands of years to cool.
 Source: geoscience.wisc.edu
Source: geoscience.wisc.edu
Each of these rocks are formed by physical changes such as melting cooling eroding compacting or deforming that are part of the rock cycle. There are three main types of rocks. Igneous crystals are formed when freely moving atoms in melted rock become arranged in orderly patterns as they cool. Above ground it is called lava. Steps of the rock cycle 1 formation of igneous rock melting cooling and crystallization magma the molten rock present deep inside the earth solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks.
 Source: eo.ucar.edu
Source: eo.ucar.edu
Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface. Cooling of igneous rocks can occur slowly beneath the surface of the earth or rapidly at its surface. Formed from magma forced into older rocks at depths within the earth s crust which then slowly solidifies below the earth s surface. Steps of the rock cycle 1 formation of igneous rock melting cooling and crystallization magma the molten rock present deep inside the earth solidifies due to cooling and crystallizes to form a type of rock called igneous rocks. Sedimentary igneous and metamorphic.
 Source: rockinrockcycle.weebly.com
Source: rockinrockcycle.weebly.com
Sedimentary rocks are formed from pieces of other existing rock or organic material. There are five sequences in the rock cycle. As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure. Each of these rocks can change into the other kinds by physical processes. Rock formed by the cooling of magma or lava.
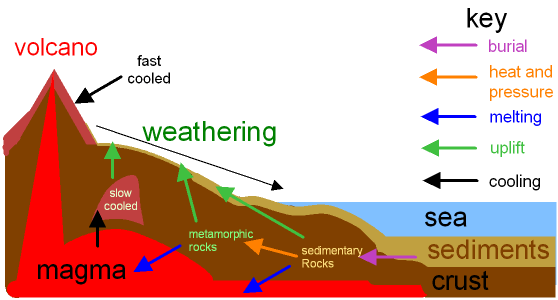 Source: gcsescience.com
Source: gcsescience.com
Above ground it is called lava. Sedimentary igneous and metamorphic. Above ground it is called lava. As melted rock cools the heat energy that allows atoms to move past one another decreases and the natural attraction between atoms causes them to stick together with similar atoms in a crystalline structure. The rock cycle is a series of processes that create and transform the types of rocks in earth s crust.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cooling in the rock cycle by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
