Explain the location of the testes in the fetal pig
Home » Science Education » Explain the location of the testes in the fetal pigExplain the location of the testes in the fetal pig
Explain The Location Of The Testes In The Fetal Pig. Recent studies have indicated that additional factors may also be required for full differentiation. The testes of males and the ovaries of females both arise from the same embryonic structures. The testes are probably located within these sacs. Ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 ch5 ch6 ch7 ch8 ch9 ch10 ch11 ch12 ch13 ch14 ch15 ch16 ch17 ch18 ch19 ch20 ch21 i ch21 ii ch22 ch23 ch24 ch25 ch26 ch27 ch28 ch29 ch30 ch31 ch32 ch33 ch34 ch35 ch36 ch37 ch38 ch39 ch40 ch41 ch42 ch43 ch44 ch45 ch46 ch47 ch48 ch49 ch50 ch51 ch52.
 Reading Fetal Pig Dissection Biology Ii Laboratory Manual From courses.lumenlearning.com
Reading Fetal Pig Dissection Biology Ii Laboratory Manual From courses.lumenlearning.com
The testes of males and the ovaries of females both arise from the same embryonic structures. Reproductive system 20 pts 1. Ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 ch5 ch6 ch7 ch8 ch9 ch10 ch11 ch12 ch13 ch14 ch15 ch16 ch17 ch18 ch19 ch20 ch21 i ch21 ii ch22 ch23 ch24 ch25 ch26 ch27 ch28 ch29 ch30 ch31 ch32 ch33 ch34 ch35 ch36 ch37 ch38 ch39 ch40 ch41 ch42 ch43 ch44 ch45 ch46 ch47 ch48 ch49 ch50 ch51 ch52. Thus in female pigs both urination and birth occur through a single urogential opening. What does the root word ectomy mean. 1 pts they are different in the way they stand.
The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis determining factor tdf the protein product of the y chromosome sry gene.
Fetal pig virtual dissection. To get to the urethra sperm travels from the testes and epididymides sing epididymis to the ductus deferentia sing deferens. The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis determining factor tdf the protein product of the y chromosome sry gene. Trace the path of food through the digestive tract of the pig. The size of the testes varies significantly depending on the age of the fetal pig. The testes of males and the ovaries of females both arise from the same embryonic structures.

Embedded within this tissue on either side is an elongated dark colored sac into which the testes descend during embryonic development. The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis determining factor tdf the protein product of the y chromosome sry gene. Embedded within this tissue on either side is an elongated dark colored sac into which the testes descend during embryonic development. Thus in female pigs both urination and birth occur through a single urogential opening. The fetal pigs that are used for the dissection are from pregnant females that.

Embedded within this tissue on either side is an elongated dark colored sac into which the testes descend during embryonic development. Thus in female pigs both urination and birth occur through a single urogential opening. The male gonad is the testis pl testes. Once dissected the atomical location is similar between the two. Recent studies have indicated that additional factors may also be required for full differentiation.

Glands e g prostate seminal vesicles add fluid to the sperm as it travels from the testes to the urethra. Once dissected the atomical location is similar between the two. What is the length of your fetal pig specimen in cm. Thus in female pigs both urination and birth occur through a single urogential opening. The fetal pigs that are used for the dissection are from pregnant females that.
 Source: hammsanatomy.weebly.com
Source: hammsanatomy.weebly.com
The vagina is located posterior to the uterus and merges with the urethra as it exits from the urinary bladder. Once dissected the atomical location is similar between the two. To get to the urethra sperm travels from the testes and epididymides sing epididymis to the ductus deferentia sing deferens. It is formed by the joining of the two uterine horns at the midline of the body. Fetal pig virtual dissection.

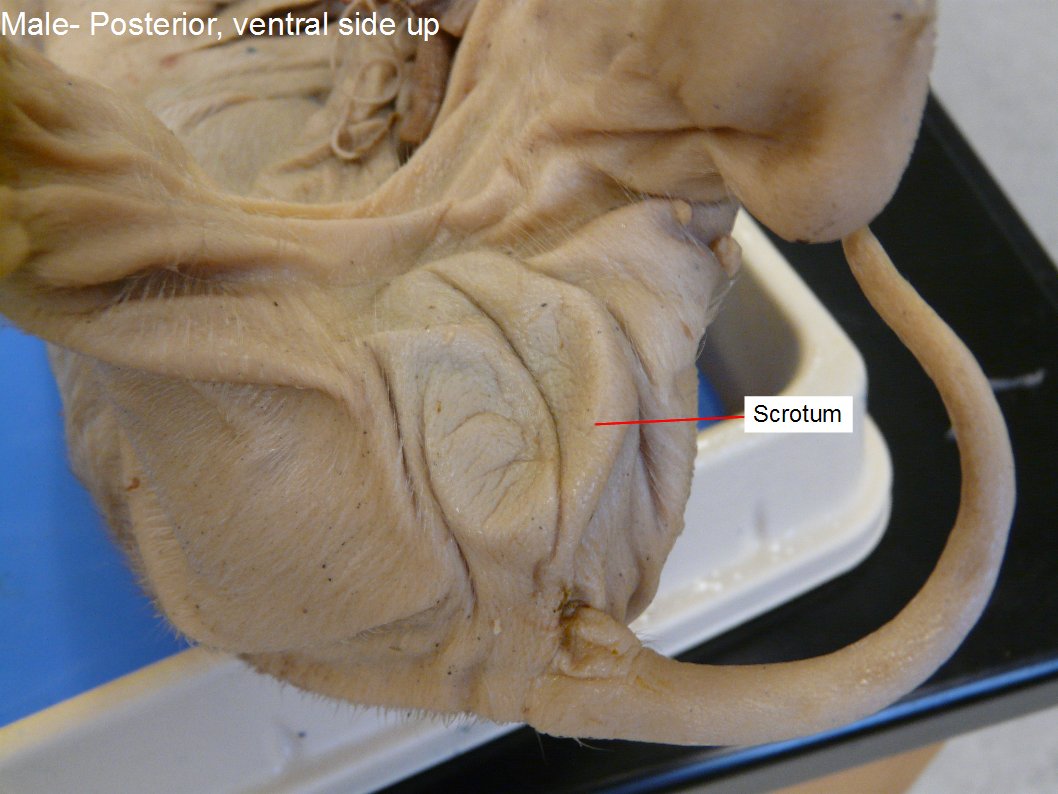
Scrotum and fascia 2. The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis determining factor tdf the protein product of the y chromosome sry gene. 1 pts they are different in the way they stand. Explain the location of the testes in the fetal pig. Embedded within this tissue on either side is an elongated dark colored sac into which the testes descend during embryonic development.

Fetal pig dissection 1. Once dissected the atomical location is similar between the two. Scrotum and fascia 2. What are the functions of the epididymis. Fetal pig dissection 1.

Ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 ch5 ch6 ch7 ch8 ch9 ch10 ch11 ch12 ch13 ch14 ch15 ch16 ch17 ch18 ch19 ch20 ch21 i ch21 ii ch22 ch23 ch24 ch25 ch26 ch27 ch28 ch29 ch30 ch31 ch32 ch33 ch34 ch35 ch36 ch37 ch38 ch39 ch40 ch41 ch42 ch43 ch44 ch45 ch46 ch47 ch48 ch49 ch50 ch51 ch52. Fetal pig dissection objective 1. The testes contain tightly coiled seminiferous tubules where sperm production takes place. What does the root word ectomy mean. What are the functions of the epididymis.

Fetal pig dissection 1. To get to the urethra sperm travels from the testes and epididymides sing epididymis to the ductus deferentia sing deferens. The size of the testes varies significantly depending on the age of the fetal pig. How do the location and the relative size of the bulbourethral glands of the fetal pig compare with those. Carefully remove tissue in the area of the hind legs on either side of your incision.

Glands e g prostate seminal vesicles add fluid to the sperm as it travels from the testes to the urethra. Trace the path of food through the digestive tract of the pig. Explain the location of the testes in the fetal pig. The male gonad is the testis pl testes. What is the length of your fetal pig specimen in cm.
 Source: oinkoinkpiggydissection.weebly.com
Source: oinkoinkpiggydissection.weebly.com
Recent studies have indicated that additional factors may also be required for full differentiation. The testes are probably located within these sacs. The teshes are now scrotay sacs ulluses posterior pelvic cavity. The testes of males and the ovaries of females both arise from the same embryonic structures. Scrotum and fascia 2.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The male gonad is the testis pl testes. Scrotum and fascia 2. The male gonad is the testis pl testes. Explain similarities and differences in the terms used to describe anatomical direction in quadrupeds pigs and bipeds humans. However the testes migrate during fetal development until they descend into the scrotal sac.

It is formed by the joining of the two uterine horns at the midline of the body. Glands e g prostate seminal vesicles add fluid to the sperm as it travels from the testes to the urethra. What 2 structures must be cut through to get to the fetal pig testes. The teshes are now scrotay sacs ulluses posterior pelvic cavity. To get to the urethra sperm travels from the testes and epididymides sing epididymis to the ductus deferentia sing deferens.
 Source: canyons.edu
Source: canyons.edu
The initial difference in male and female gonad development are dependent on testis determining factor tdf the protein product of the y chromosome sry gene. Trace the path of food through the digestive tract of the pig. Ch1 ch2 ch3 ch4 ch5 ch6 ch7 ch8 ch9 ch10 ch11 ch12 ch13 ch14 ch15 ch16 ch17 ch18 ch19 ch20 ch21 i ch21 ii ch22 ch23 ch24 ch25 ch26 ch27 ch28 ch29 ch30 ch31 ch32 ch33 ch34 ch35 ch36 ch37 ch38 ch39 ch40 ch41 ch42 ch43 ch44 ch45 ch46 ch47 ch48 ch49 ch50 ch51 ch52. What are the functions of the epididymis. The male gonad is the testis pl testes.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The teshes are now scrotay sacs ulluses posterior pelvic cavity. To get to the urethra sperm travels from the testes and epididymides sing epididymis to the ductus deferentia sing deferens. Fetal pig dissection objective 1. The size of the testes varies significantly depending on the age of the fetal pig. As with the ovaries the testes serve a second function to produce sex hormones like testosterone.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
What is the length of your fetal pig specimen in cm. What does the root word ectomy mean. The vagina is located posterior to the uterus and merges with the urethra as it exits from the urinary bladder. The size of the testes varies significantly depending on the age of the fetal pig. Embedded within this tissue on either side is an elongated dark colored sac into which the testes descend during embryonic development.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title explain the location of the testes in the fetal pig by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
