Gram stains of common bacteria
Home » Science Education » Gram stains of common bacteriaGram stains of common bacteria
Gram Stains Of Common Bacteria. When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial.
 Gram Stain For Bacterial Identification Health Disease Diet Food And Fitness From healthwebsite.net
Gram Stain For Bacterial Identification Health Disease Diet Food And Fitness From healthwebsite.net
The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e.
Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial.
Therefore these cells stain purple. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain. Coli atcc 11775 gram negative bacilli in red the most common gram stain reference bacteria. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. Therefore these cells stain purple. Coli atcc 11775 gram negative bacilli in red the most common gram stain reference bacteria. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e.
 Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Therefore these cells stain purple.
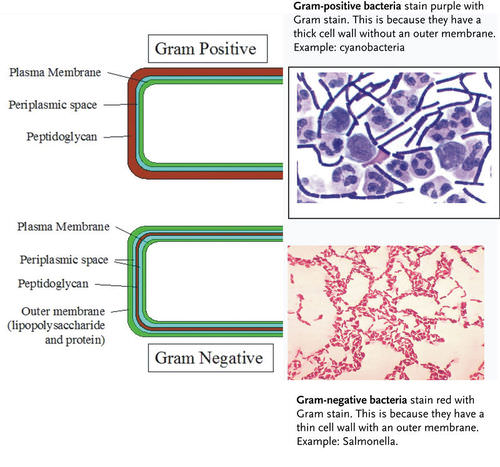
Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial. Coli atcc 11775 gram negative bacilli in red the most common gram stain reference bacteria. When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. Therefore these cells stain purple. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e.
 Source: iitway.com
Source: iitway.com
Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet. Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain.
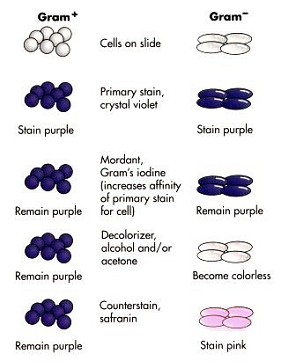 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol.
 Source: healthwebsite.net
Source: healthwebsite.net
Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e. Gram stain or gram staining also called gram s method is a method of staining used to distinguish and classify bacterial. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple.
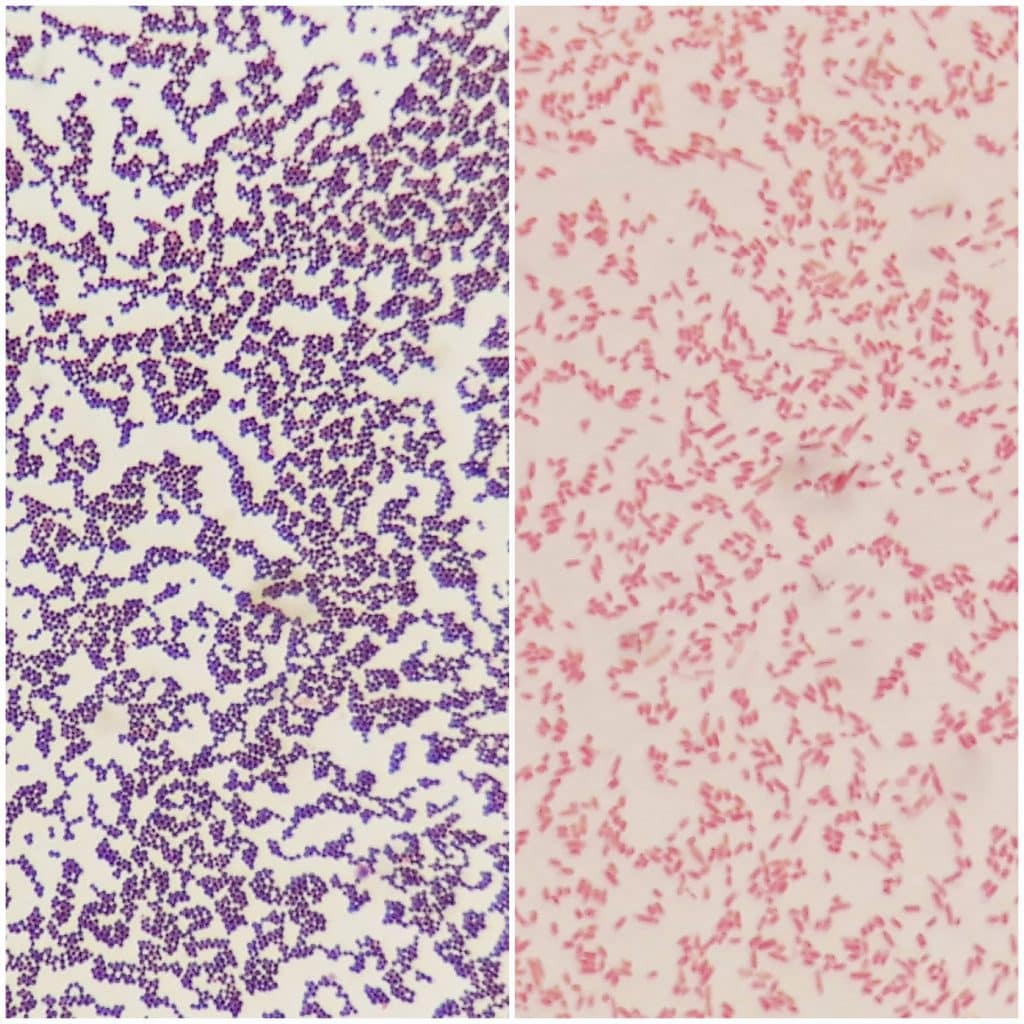 Source: teachmephysiology.com
Source: teachmephysiology.com
When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. Coli atcc 11775 gram negative bacilli in red the most common gram stain reference bacteria. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. Therefore these cells stain purple.
 Source: tmedweb.tulane.edu
Source: tmedweb.tulane.edu
In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. The gram stain involves staining bacteria fixing the color with a mordant decolorizing the cells and applying a counterstain. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Therefore these cells stain purple. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. Therefore these cells stain purple. In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents. Both gram positive and gram negative cells have peptidoglycan in their cell walls so initially all bacteria stain violet.
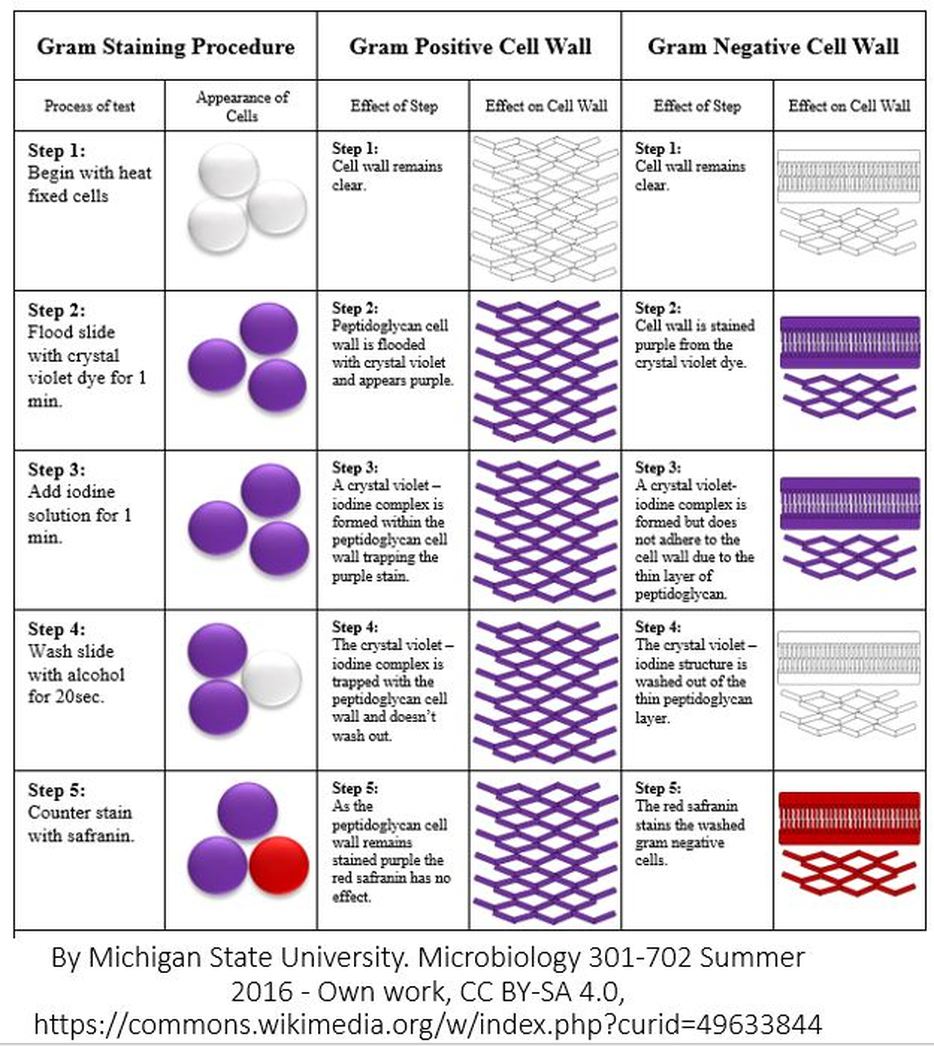 Source: scientistcindy.com
Source: scientistcindy.com
When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. Coli atcc 11775 gram negative bacilli in red the most common gram stain reference bacteria. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet.
 Source: cnx.org
Source: cnx.org
In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. Therefore these cells stain purple. In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
When acetone is added these lipids dissolve exposing the relatively thin peptidoglycan membrane. The primary stain crystal violet binds to peptidoglycan coloring cells purple. When safranin is added it is retained but obscured by the crystal violet. The gram stain procedure distinguishes between gram positive and gram negative groups by coloring these cells red or violet. Gram staining is a common technique used to differentiate two large groups of bacteria based on their different cell wall constituents.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Gram positive organisms have a thick cell wall of peptidoglycan and so retain the crystal violet stain when washed with acetone methanol. Therefore these cells stain purple. In contrast gram negative organisms have an outer lipopolysaccharide layer. A gram stain of mixed staphylococcus aureus s. Aureus atcc 25923 gram positive cocci in purple and escherichia coli e.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title gram stains of common bacteria by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
