Hot air balloon physics
Home » Science Education » Hot air balloon physicsHot air balloon physics
Hot Air Balloon Physics. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon. This hot air balloon physics article by william phillips was originally printed in ballooning magazine. Gianna barada newton s first law an object at rest.
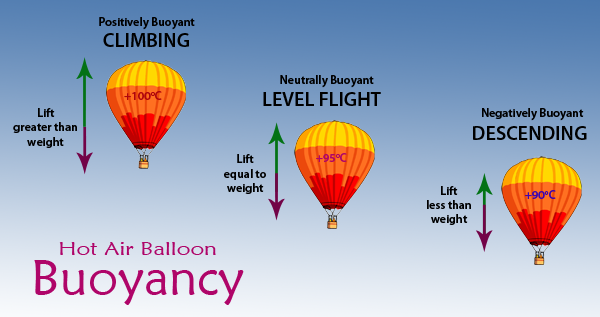 How Hot Air Balloons Fly From brisbanehotairballooning.com.au
How Hot Air Balloons Fly From brisbanehotairballooning.com.au
ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon. Hot air balloons float due to the heated air inside the envelope having a lower density than the colder air outside. The physics of hot air balloon flight whilst quite simple is often poorly understood. Hot air balloon physics how a hot air balloon flys. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude.
I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape.
Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. The greater the mass the more buoyancy force there needs to be. Begingroup thanks so much for your answer. A hot air balloon is a special kind of lighter than air aircraft which simply flies because of hot air rises. Hot air balloons have a special valve that lets some air come into the balloon without all too much coming in and causing the balloon to fall fast. ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon.
 Source: aviation.stackexchange.com
Source: aviation.stackexchange.com
A hot air balloon is a very simple type of aircraft that you can use to fly from one place to another. Hot air balloon physics how a hot air balloon flys. Hot air balloons float due to the heated air inside the envelope having a lower density than the colder air outside. Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
This really breaks down the problem very nicely. Begingroup thanks so much for your answer. That is buyouncy and charle s law of thermodynamics. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon. Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws.
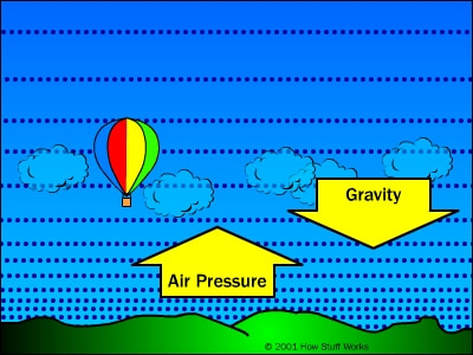 Source: mkhotairballoonproject.weebly.com
Source: mkhotairballoonproject.weebly.com
This hot air balloon physics article by william phillips was originally printed in ballooning magazine. Hot air balloons have a special valve that lets some air come into the balloon without all too much coming in and causing the balloon to fall fast. Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon. ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon.
 Source: blog.mrmeyer.com
Source: blog.mrmeyer.com
It takes a long time for the air in the balloon to cool down all the way so you usually let air back in. A hot air balloon with volume 10 m 3 353 ft 3 is heated to 100 o c 212 o f. I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape. Hot air balloons have a special valve that lets some air come into the balloon without all too much coming in and causing the balloon to fall fast. Adam published on 10 22 2007.
 Source: prezi.com
Source: prezi.com
That is buyouncy and charle s law of thermodynamics. I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape. That is buyouncy and charle s law of thermodynamics. Hot air balloons float due to the heated air inside the envelope having a lower density than the colder air outside. The greater the mass the more buoyancy force there needs to be.
 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
This hot air balloon physics article by william phillips was originally printed in ballooning magazine. The physics of hot air balloon flight whilst quite simple is often poorly understood. A hot air balloon with volume 10 m 3 353 ft 3 is heated to 100 o c 212 o f. I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape. Adam published on 10 22 2007.
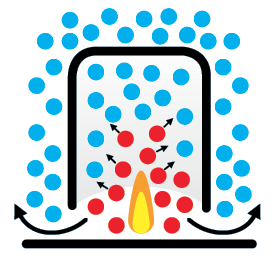 Source: howitworksdaily.com
Source: howitworksdaily.com
The physics of hot air balloons newtons 2nd law force mass x acceleration the more mass that a hot air balloon has to hold the slower it will travel. Adam published on 10 22 2007. The physics of hot air balloon flight whilst quite simple is often poorly understood. Gianna barada newton s first law an object at rest. That is buyouncy and charle s law of thermodynamics.
 Source: brisbanehotairballooning.com.au
Source: brisbanehotairballooning.com.au
Operating a hot air balloon requires specialised knowledge and skill. This hot air balloon physics article by william phillips was originally printed in ballooning magazine. I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape. Operating a hot air balloon requires specialised knowledge and skill. The physics of hot air balloon flight whilst quite simple is often poorly understood.
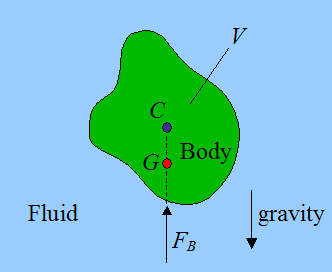 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
A hot air balloon is a very simple type of aircraft that you can use to fly from one place to another. A hot air balloon is a special kind of lighter than air aircraft which simply flies because of hot air rises. A hot air balloon is a very simple type of aircraft that you can use to fly from one place to another. Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Begingroup thanks so much for your answer. Hot air balloons have a special valve that lets some air come into the balloon without all too much coming in and causing the balloon to fall fast. Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. Gianna barada newton s first law an object at rest. Operating a hot air balloon requires specialised knowledge and skill.
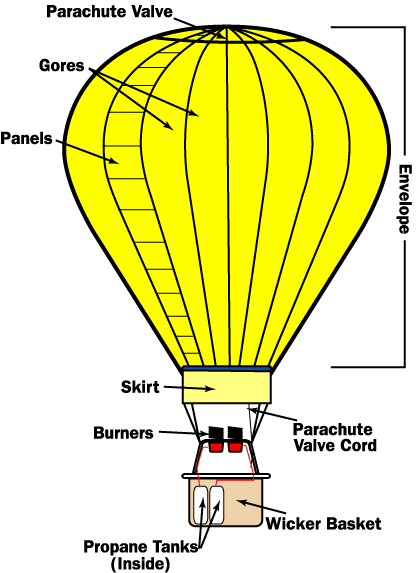 Source: ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu
Source: ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu
This really breaks down the problem very nicely. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. A hot air balloon with volume 10 m 3 353 ft 3 is heated to 100 o c 212 o f. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon.
 Source: flatearth.ws
Source: flatearth.ws
Begingroup thanks so much for your answer. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. The physics of hot air balloons newtons 2nd law force mass x acceleration the more mass that a hot air balloon has to hold the slower it will travel. ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon. Gianna barada newton s first law an object at rest.
 Source: askeyphysics.org
Source: askeyphysics.org
Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude. Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude. It takes a long time for the air in the balloon to cool down all the way so you usually let air back in. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon. This really breaks down the problem very nicely.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Using simple laws of physics one can travel in the basket suspended from a balloon and enjoy the beautiful view instead of being inside an aeroplane that flies much faster and at a much higher altitude. I m just looking at coding out a predictor so i believe for my purposes hot air balloon with large drag coefficient and people likely won t take one up in crazy wind shear the balloon speed could equal wind speed but this wouldn t be the case for something with a different shape. In the same way that a boat is supported by water on the ocean it is cold air supporting a hot air balloon. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. Hot air balloon physics operation if the balloon operator wishes to lower the hot air balloon he can either stop firing the burner which causes the hot air in the envelope to cool decreasing the buoyant force or he opens a small vent at the top of the balloon envelope via a control line.
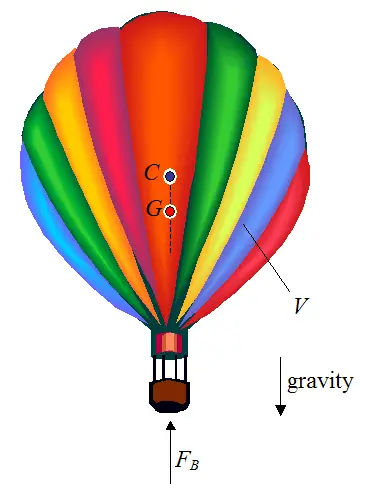 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Its working principle is solely based on two physical laws. This really breaks down the problem very nicely. ρ h density hot balloon air kg m 3 slugs ft 3 a g acceleration of gravity 9 81 m s 2 32 174 ft s 2 example lifting force created by a hot air balloon. Operating a hot air balloon requires specialised knowledge and skill. The physics of hot air balloon flight whilst quite simple is often poorly understood.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title hot air balloon physics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
