How stuff works roller coaster physics
Home » Science Education » How stuff works roller coaster physicsHow stuff works roller coaster physics
How Stuff Works Roller Coaster Physics. But needless to say they all involve going around loops bends and twists at high speed. But what about that sinking feeling. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. Presents the full text of the article entitled how roller coasters work by tom harris.
 Roller Coasters The Dynamics Of Amusement Parks From dynamicsofamusementparks.weebly.com
Roller Coasters The Dynamics Of Amusement Parks From dynamicsofamusementparks.weebly.com
When you are riding in a coaster car that is traveling at a constant speed you only feel the downward force of gravity. Gravity plays a huge part in roller coaster physics. Brave falling rocks kick off booster rockets and destroy physical structures on the way to the finish line. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. Presents the full text of the article entitled how roller coasters work by tom harris. The other force acting on you is acceleration.
Physics in motion strap yourself to a rocket and get ready to experience serious g forces.
The typical roller coaster works by gravity. How roller coasters work how stuff works roller coasters give riders the experience of flying as they shoot riders down long stretches of spiraled tracks. At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. Roller coasters are driven almost entirely by basic inertial gravitational and centripetal forces all manipulated in the service of a great ride. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy.
 Source: www2.oakwood.k12.oh.us
Source: www2.oakwood.k12.oh.us
One can best gain an appreciation of roller coaster physics by riding on a roller coaster and experiencing the thrill of the ride. Brave falling rocks kick off booster rockets and destroy physical structures on the way to the finish line. How roller coasters work how stuff works roller coasters give riders the experience of flying as they shoot riders down long stretches of spiraled tracks. The author discusses the physics of roller coasters. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a. But what about that sinking feeling. The author discusses the physics of roller coasters.
 Source: goodreads.com
Source: goodreads.com
The author discusses the physics of roller coasters. The other force acting on you is acceleration. But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. The typical roller coaster works by gravity. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors.

The author discusses the physics of roller coasters. But make sure to hit the brakes before the end of the track. Harris details potential energy kinetic energy the wooden and steel roller coaster tracks the braking system and the effects on the body from the acceleration force. One can best gain an appreciation of roller coaster physics by riding on a roller coaster and experiencing the thrill of the ride. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy.
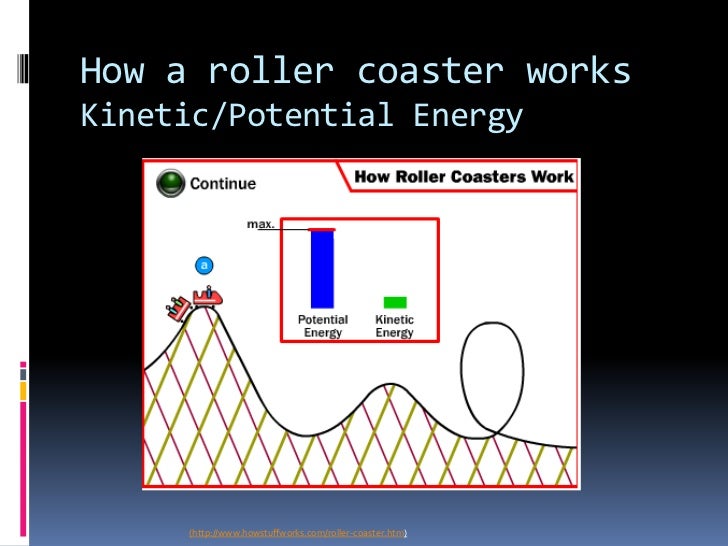 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
There are many variations on roller coaster design. Harris details potential energy kinetic energy the wooden and steel roller coaster tracks the braking system and the effects on the body from the acceleration force. When you are riding in a coaster car that is traveling at a constant speed you only feel the downward force of gravity. The other force acting on you is acceleration. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed.
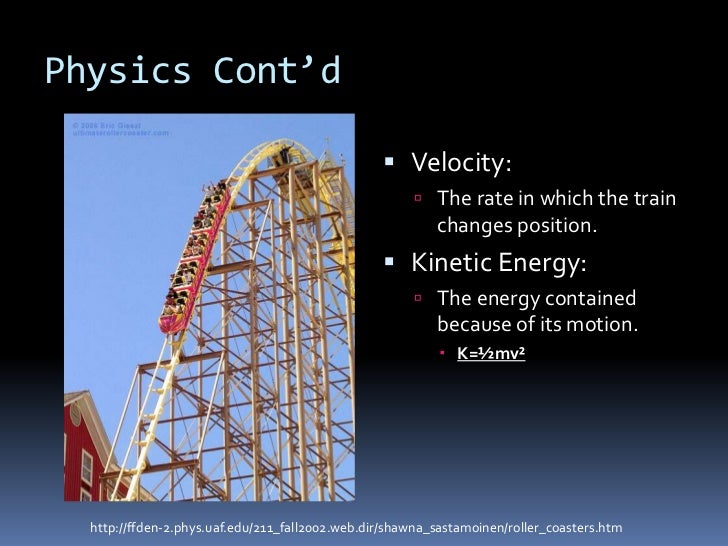 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
But what about that sinking feeling. But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. The typical roller coaster works by gravity. When you are riding in a coaster car that is traveling at a constant speed you only feel the downward force of gravity.
 Source: wonderopolis.org
Source: wonderopolis.org
At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. As a coaster gets higher gravity can pull the cars down faster and faster to push them along the tracks. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy. There are many variations on roller coaster design. Ignite the rocket and launch a timed run down a 6 mile track.
 Source: mymommystyle.com
Source: mymommystyle.com
There are many variations on roller coaster design. At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. The purpose of the coaster s initial ascent is to build up a sort of reservoir of potential energy. The constant change in direction and the constant change in speed. Roller coasters are driven almost entirely by basic inertial gravitational and centripetal forces all manipulated in the service of a great ride.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance. One can best gain an appreciation of roller coaster physics by riding on a roller coaster and experiencing the thrill of the ride. But needless to say they all involve going around loops bends and twists at high speed.
 Source: sciencemadefun.net
Source: sciencemadefun.net
The other force acting on you is acceleration. When you are riding in a coaster car that is traveling at a constant speed you only feel the downward force of gravity. Harris details potential energy kinetic energy the wooden and steel roller coaster tracks the braking system and the effects on the body from the acceleration force. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance.
 Source: dynamicsofamusementparks.weebly.com
Source: dynamicsofamusementparks.weebly.com
A rightward moving roller coaster car gradually becomes an upward moving roller coaster car and a leftward moving roller coaster car then a downward moving roller coaster car. Physics in motion strap yourself to a rocket and get ready to experience serious g forces. How roller coasters work how stuff works roller coasters give riders the experience of flying as they shoot riders down long stretches of spiraled tracks. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a.
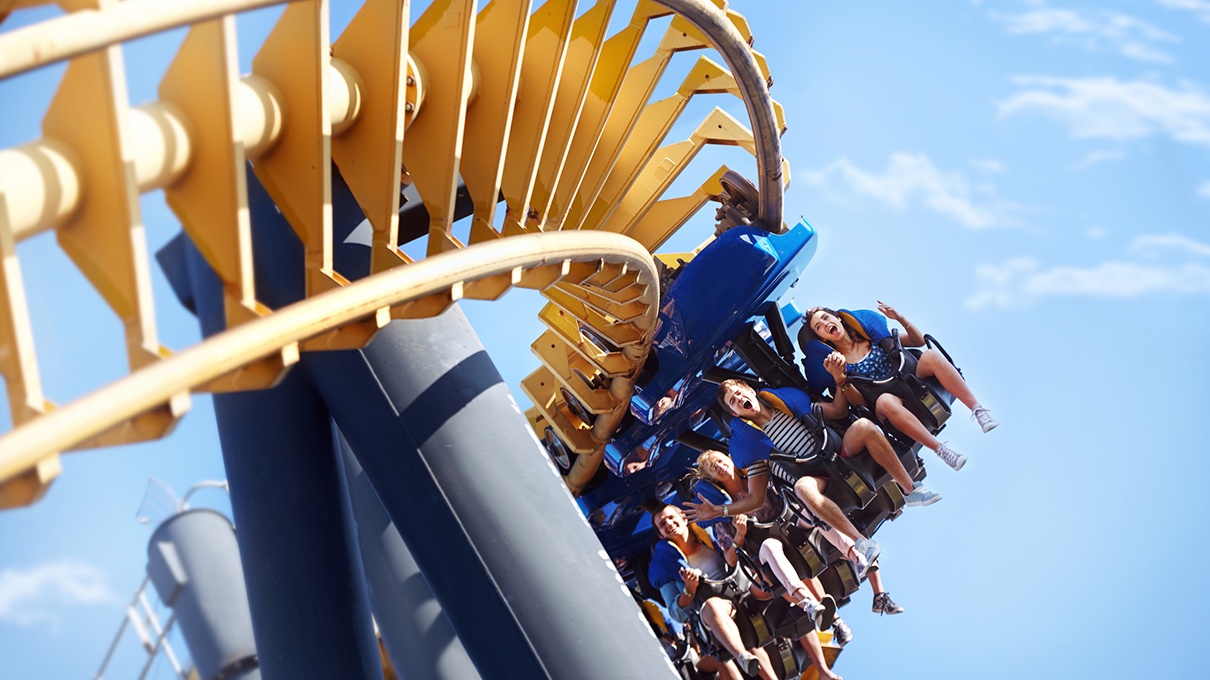 Source: science.howstuffworks.com
Source: science.howstuffworks.com
There are many variations on roller coaster design. A roller coaster usually begins with a mechanical device such as a chain and motor which exerts a. There are many variations on roller coaster design. The typical roller coaster works by gravity. Ignite the rocket and launch a timed run down a 6 mile track.
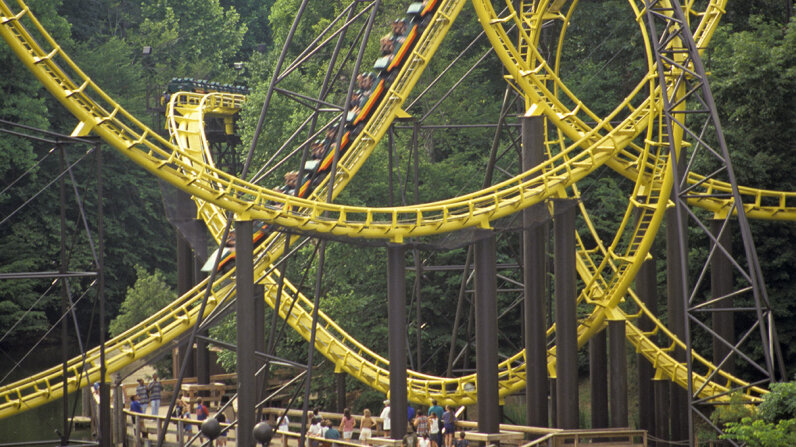 Source: science.howstuffworks.com
Source: science.howstuffworks.com
Find out why it occurs. But as the car speeds up or slows down you feel pressed against your seat or the restraining bar. Brave falling rocks kick off booster rockets and destroy physical structures on the way to the finish line. At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. Ignite the rocket and launch a timed run down a 6 mile track.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Ignite the rocket and launch a timed run down a 6 mile track. Roller coasters are almost entirely driven by different forces of inertia gravity and centripetal. But make sure to hit the brakes before the end of the track. Harris details potential energy kinetic energy the wooden and steel roller coaster tracks the braking system and the effects on the body from the acceleration force. The physics of a roller coaster also involves work energy friction inertia and air resistance.
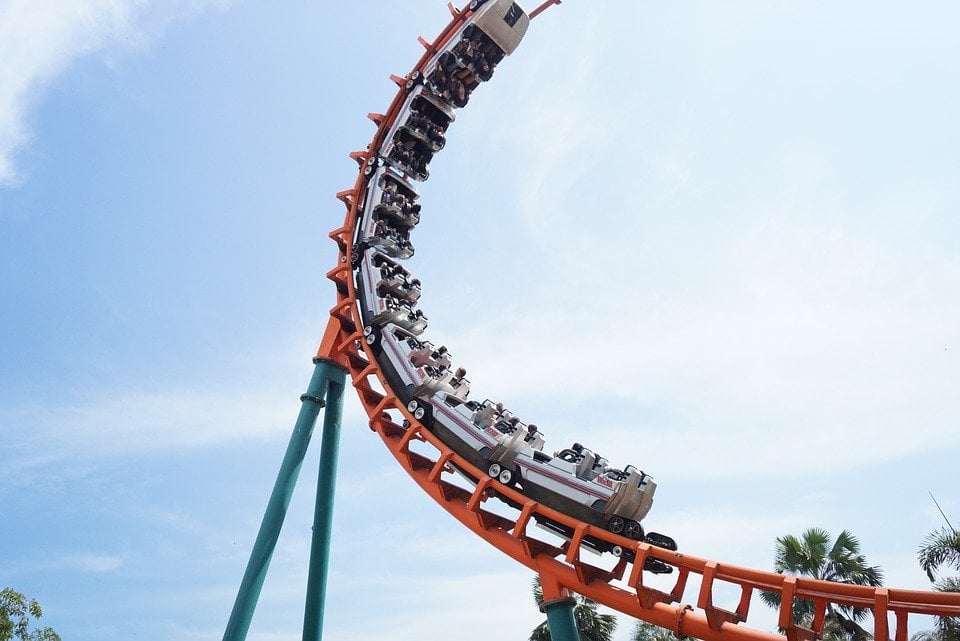 Source: scienceabc.com
Source: scienceabc.com
The typical roller coaster works by gravity. Physics in motion strap yourself to a rocket and get ready to experience serious g forces. Brave falling rocks kick off booster rockets and destroy physical structures on the way to the finish line. At every point on a roller coaster ride gravity is pulling you straight down. As the roller coaster cart passes through the clothoid loop one experiences acceleration based on two main factors.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how stuff works roller coaster physics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
