Layers of the retina and their function
Home » Science Education » Layers of the retina and their functionLayers of the retina and their function
Layers Of The Retina And Their Function. Retinal microanatomy retina is composed of 10 micro layers sclerad to vitread retinal pigment epithelium. Retinal pigment epithelium this is a single layer of cells that provide essential nutrition and waste removal for the photoreceptor cells. The primary light sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells which are of two types. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones.
 Layers Of The Retina Discovery Eye Foundation From discoveryeye.org
Layers Of The Retina Discovery Eye Foundation From discoveryeye.org
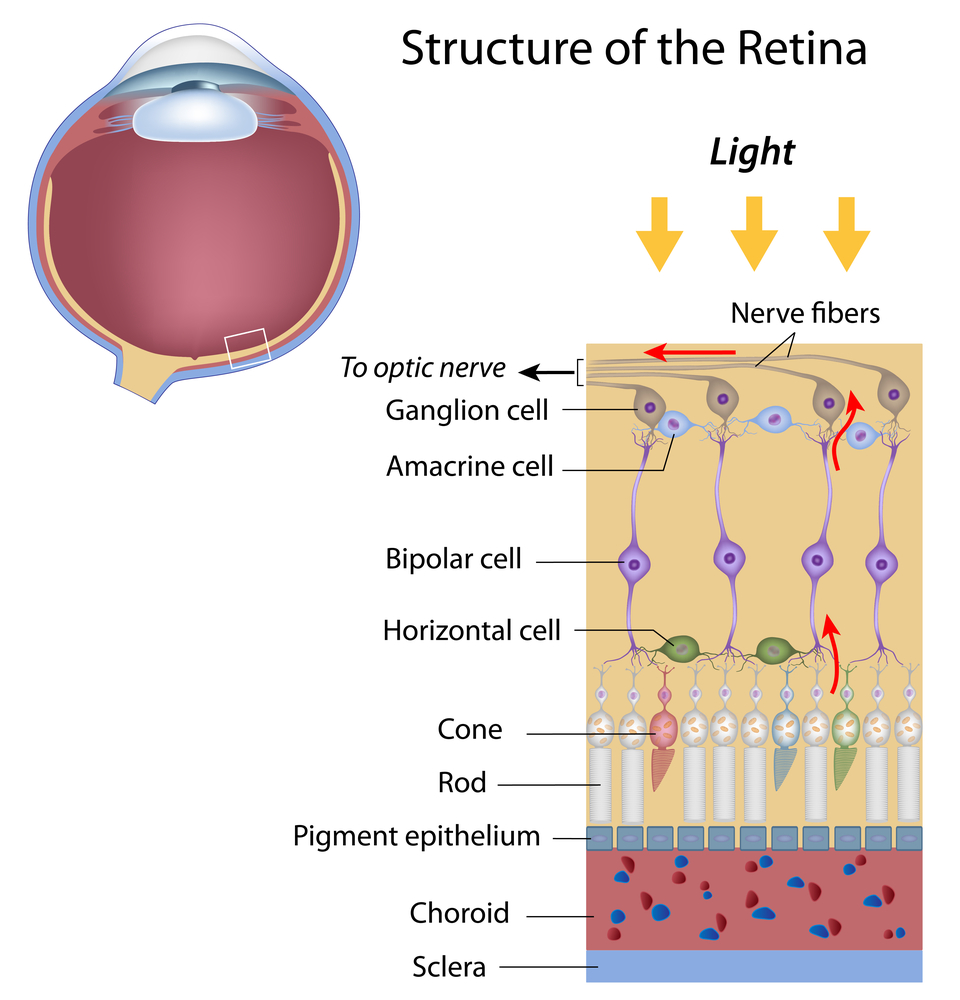
The layers of the retina in the order light strikes them are the optic nerve fiber layer ganglion cell layer inner synaptic layer bipolar cell layer outer synaptic layer layer of rods and cones and pigment epithelium. It is located near the optic nerve. The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia. This area of the eye is responsible for receiving images from the outside to transform them into nerve signals that will be transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. Outer plexiform layer 6. The retina is a complex sensory membrane located on the back surface of the innermost layer of the eyeball.
Ganglion cell layer 9.
External limiting membrane 4. Ganglion cell layer 9. Retina is the innermost layer of the eyeball. Inner nuclear layer 7. The layers of the retina in the order light strikes them are the optic nerve fiber layer ganglion cell layer inner synaptic layer bipolar cell layer outer synaptic layer layer of rods and cones and pigment epithelium. Layers of the retina.
 Source: quora.com
Source: quora.com
The primary light sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells which are of two types. The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia. Ganglion cells are present closest to the vitreous body. This area of the eye is responsible for receiving images from the outside to transform them into nerve signals that will be transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones.
 Source: webvision.med.utah.edu
Source: webvision.med.utah.edu
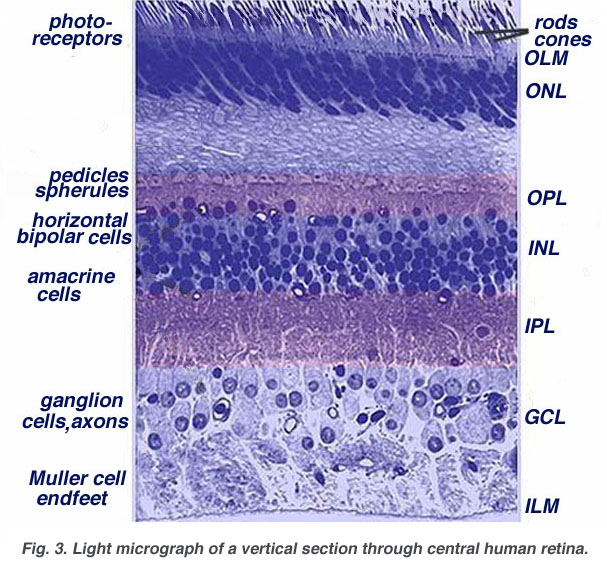
It is located near the optic nerve. The primary light sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells which are of two types. Retina is the innermost layer of the eyeball. It is the light sensitive layer of the eye and acts as a film of a camera where an image is formed. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones.
 Source: heidelbergengineering.co.uk
Source: heidelbergengineering.co.uk
Ganglion cell layer 9. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. The retina is actually an extension of the brain formed embryonically from neural tissue and connected to the brain proper by the optic nerve. The retina is a complex sensory membrane located on the back surface of the innermost layer of the eyeball. Outer plexiform layer 6.
 Source: discoveryeye.org
Source: discoveryeye.org
Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones. The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. This area of the eye is responsible for receiving images from the outside to transform them into nerve signals that will be transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. The retina is actually an extension of the brain formed embryonically from neural tissue and connected to the brain proper by the optic nerve. It is located near the optic nerve.
 Source: medcell.med.yale.edu
Source: medcell.med.yale.edu
Choroid this is made up of a layer of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the retina. It is located near the optic nerve. The primary light sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells which are of two types. The retina is actually an extension of the brain formed embryonically from neural tissue and connected to the brain proper by the optic nerve. Retina is the innermost layer of the eyeball.
 Source: cz.pinterest.com
Source: cz.pinterest.com
The primary light sensing cells in the retina are the photoreceptor cells which are of two types. Retina layer of nervous tissue that covers the inside of the back two thirds of the eyeball in which stimulation by light occurs initiating the sensation of vision. Choroid this is made up of a layer of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the retina. This area of the eye is responsible for receiving images from the outside to transform them into nerve signals that will be transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve. The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Accumulation of waste can lead to amd and stargardt disease. Inner plexiform layer 8. Retina layer of nervous tissue that covers the inside of the back two thirds of the eyeball in which stimulation by light occurs initiating the sensation of vision. The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia. The retina is a complex sensory membrane located on the back surface of the innermost layer of the eyeball.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Inner plexiform layer 8. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black and white vision. Outer plexiform layer 6. The layers of the retina in the order light strikes them are the optic nerve fiber layer ganglion cell layer inner synaptic layer bipolar cell layer outer synaptic layer layer of rods and cones and pigment epithelium. Ganglion cells are present closest to the vitreous body.
 Source: kenhub.com
Source: kenhub.com
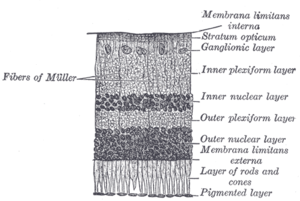
The layers of the retina in the order light strikes them are the optic nerve fiber layer ganglion cell layer inner synaptic layer bipolar cell layer outer synaptic layer layer of rods and cones and pigment epithelium. The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. It is primarily made up of three layers of nerve cells these are ganglion cells bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones. External limiting membrane 4.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia. Ganglion cells are present closest to the vitreous body. Read more on this topic. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones. The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia.
 Source: doctorlib.info
Source: doctorlib.info
The retina is normally red reflecting blood flow and is pale in anemia or ischemia. Defect in the chm gene can cause choroideremia leaky blood vessels can expand in the retina causing wet age related macular degeneration amd and diabetic retinopathy. The retina is a complex sensory membrane located on the back surface of the innermost layer of the eyeball. Inner nuclear layer 7. It is the light sensitive layer of the eye and acts as a film of a camera where an image is formed.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
It is the light sensitive layer of the eye and acts as a film of a camera where an image is formed. The retina is a thin layer of tissue that lines the back of the eye on the inside. Retina layer of nervous tissue that covers the inside of the back two thirds of the eyeball in which stimulation by light occurs initiating the sensation of vision. Rods function mainly in dim light and provide black and white vision. Ganglion cell layer 9.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
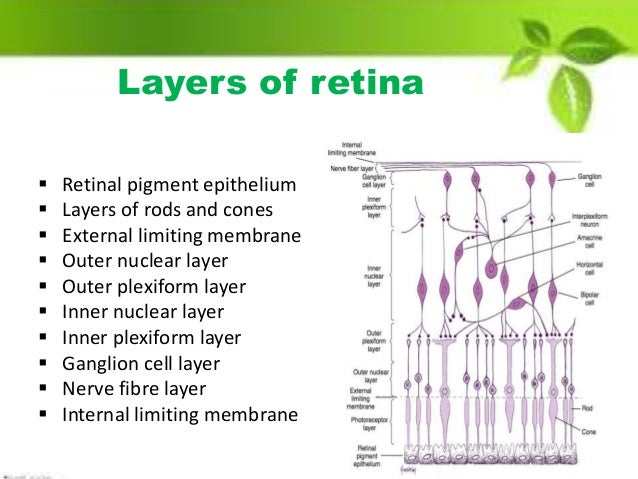
Ganglion cells are present closest to the vitreous body. The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused. Outer nuclear layer 5. It is primarily made up of three layers of nerve cells these are ganglion cells bipolar cells and photoreceptor cells. Photoreceptor layer of rods and cones.
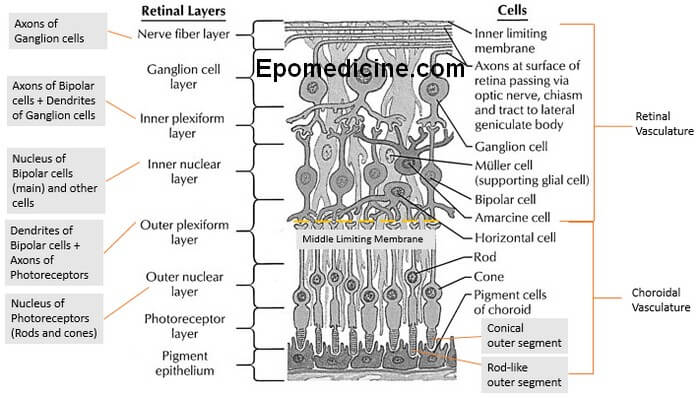 Source: epomedicine.com
Source: epomedicine.com
The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused. The neural retina consists of several layers of neurons interconnected by synapses and is supported by an outer layer of pigmented epithelial cells. Nerve fiber layer 10. Choroid this is made up of a layer of blood vessels that supply oxygen and nutrients to the retina. The purpose of the retina is to receive light that the lens has focused.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The retina is a complex sensory membrane located on the back surface of the innermost layer of the eyeball. Layers of the retina. Inner nuclear layer 7. Ganglion cell layer 9. Outer plexiform layer 6.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title layers of the retina and their function by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
