Light refraction rainbow
Home » Science Education » Light refraction rainbowLight refraction rainbow
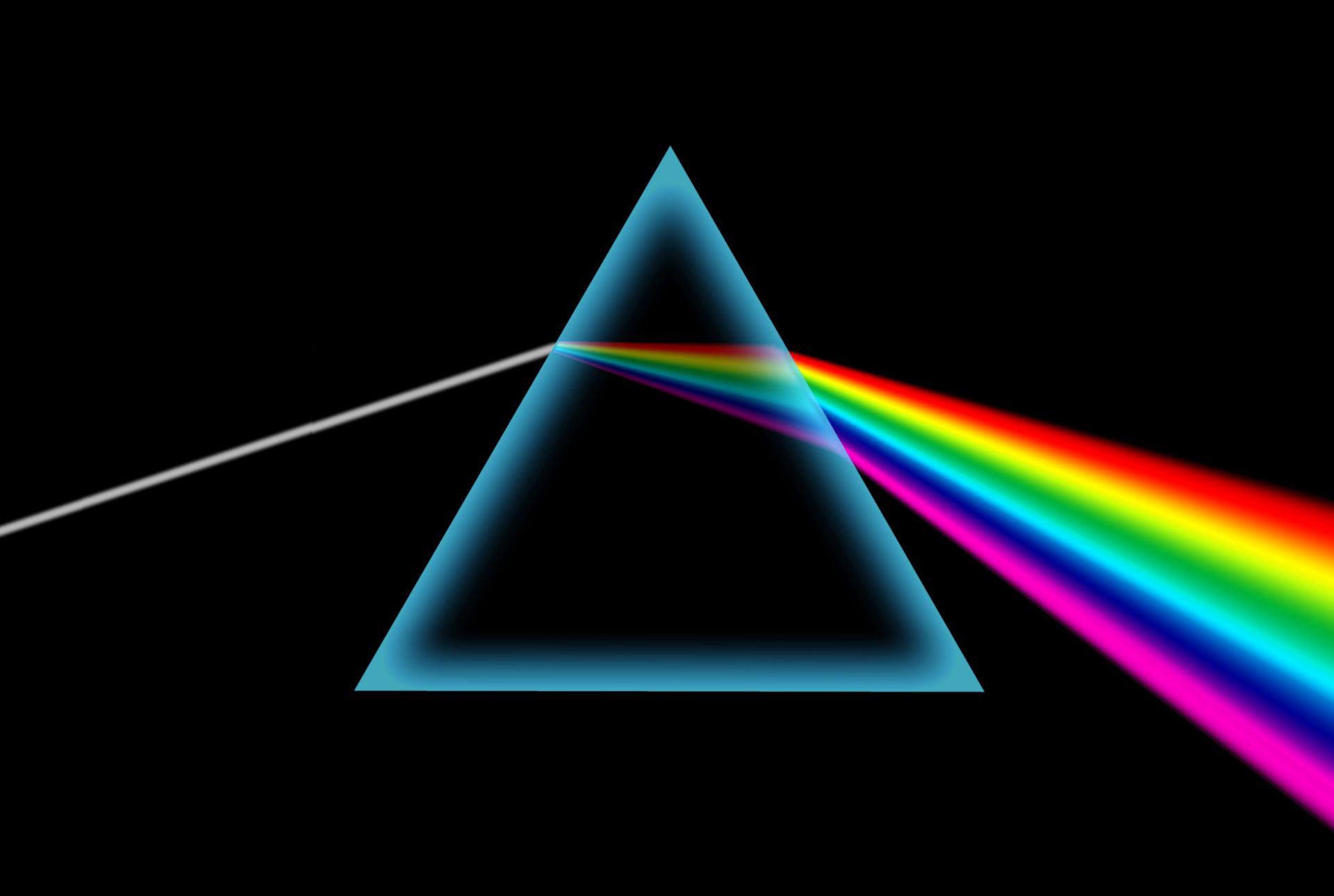
Light Refraction Rainbow. The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. Refraction is also responsible for rainbows and for the splitting of white light into a rainbow spectrum as it passes through a glass prism glass has a higher refractive index than air. Rainbows can be full circles. When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs in which different coloured components.
 What S In A Rainbow Let S Talk Science From letstalkscience.ca
What S In A Rainbow Let S Talk Science From letstalkscience.ca
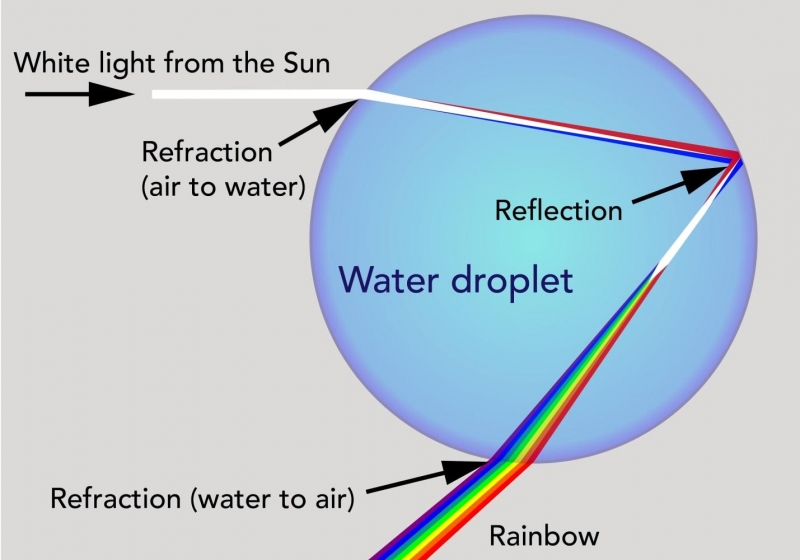
When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs in which different coloured components. Light bends or more accurately changes directions when it travels from one medium to another. A rainbow is formed when light generally sunlight passes through water droplets hanging in the atmosphere. A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves.
Since the index of refraction of water varies with wavelength the light is dispersed and a rainbow is observed as shown in figure 5a.
To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun. Since the index of refraction of water varies with wavelength the light is dispersed and a rainbow is observed as shown in figure 5a. The light waves change direction as they pass through the water droplets resulting in two processes.
 Source: rookieparenting.com
Source: rookieparenting.com
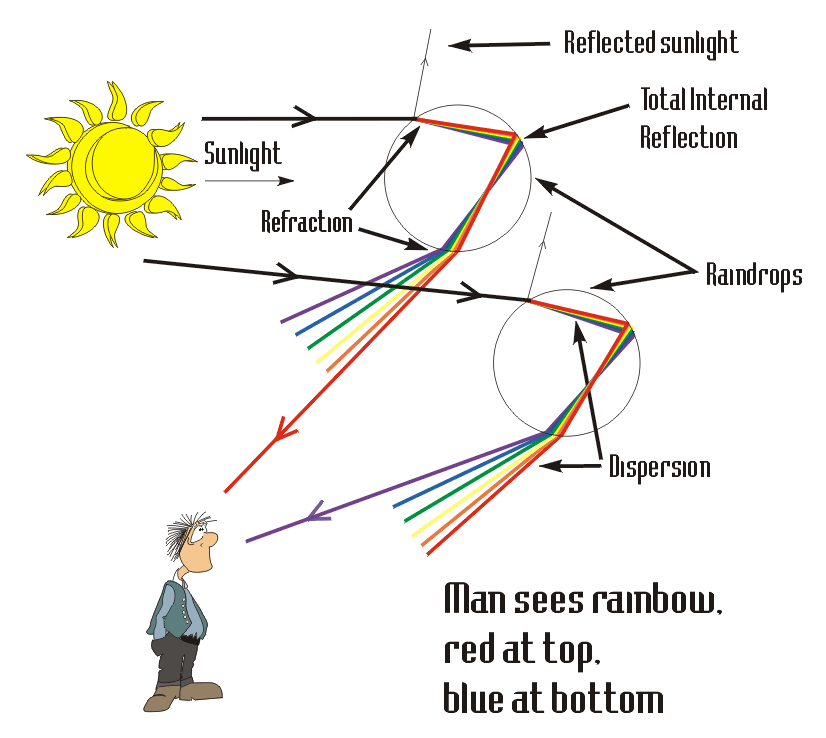
Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun. According to descartes calculations using laws of optics the three stage refraction reflection refraction pattern that light undergoes when passing through a raindrop produces a concentration of outgoing rays along a line that is 42 degrees above the head of an observer s shadow. Since the index of refraction of water varies with wavelength the light is dispersed and a rainbow is observed as shown in figure 5a. In nature a rainbow is formed when sunlight is refracted on entering a droplet of water reflected inside the back of the droplet and finally refracted again on leaving the droplet. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist.
 Source: rebeccapaton.net
Source: rebeccapaton.net
A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day. A rainbow is an excellent demonstration of the dispersion of light and one more piece of evidence that visible light is composed of a spectrum of wavelengths each associated with a distinct color. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves. According to descartes calculations using laws of optics the three stage refraction reflection refraction pattern that light undergoes when passing through a raindrop produces a concentration of outgoing rays along a line that is 42 degrees above the head of an observer s shadow.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. This happens because light travels at different speeds in different mediums. Light bends or more accurately changes directions when it travels from one medium to another. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun.
 Source: socratic.org
Source: socratic.org
This dispersion of light allows us to see the spectrum of colors that form a rainbow 2. This concentration of light rays is the rainbow that we see. Light enters a drop of water and is reflected from the back of the drop as shown in figure 4. This second reflection causes the colours on the secondary rainbow to be reversed. One of nature s most splendid masterpieces is the rainbow.
 Source: letstalkscience.ca
Source: letstalkscience.ca
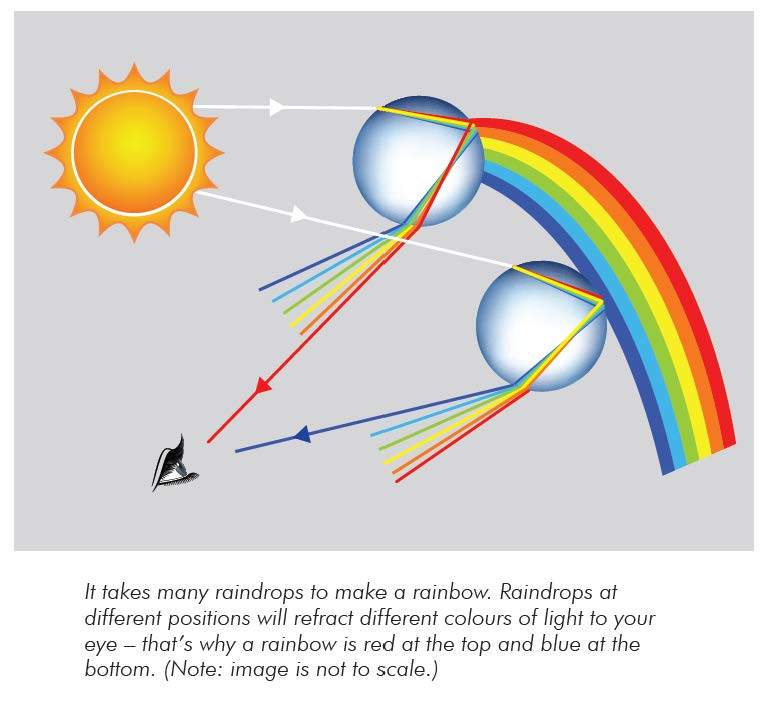
The fundamental process at work in a rainbow is refraction the bending of light. The fundamental process at work in a rainbow is refraction the bending of light. A rainbow is formed when light generally sunlight passes through water droplets hanging in the atmosphere. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun.
 Source: insidetheperimeter.ca
Source: insidetheperimeter.ca
This second reflection causes the colours on the secondary rainbow to be reversed. In nature a rainbow is formed when sunlight is refracted on entering a droplet of water reflected inside the back of the droplet and finally refracted again on leaving the droplet. A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day. When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs in which different coloured components. A rainbow is formed when light generally sunlight passes through water droplets hanging in the atmosphere.
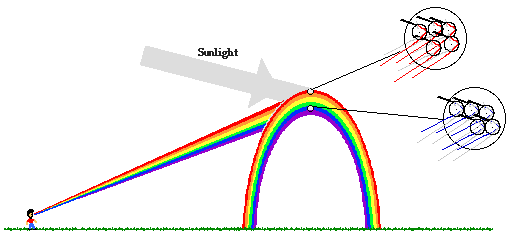 Source: physicsclassroom.com
Source: physicsclassroom.com
However the observer normally sees only an arc formed by illuminated droplets above the ground and centered on a line from the sun to the observer. When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs in which different coloured components. Refraction is also responsible for rainbows and for the splitting of white light into a rainbow spectrum as it passes through a glass prism glass has a higher refractive index than air. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. The light waves change direction as they pass through the water droplets resulting in two processes.
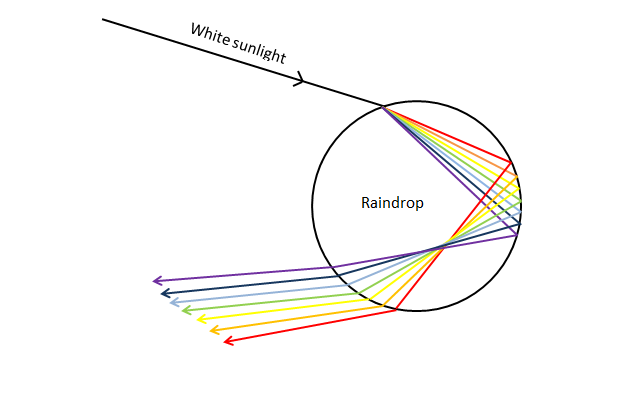 Source: blog.metservice.com
Source: blog.metservice.com
The light waves change direction as they pass through the water droplets resulting in two processes. One of nature s most splendid masterpieces is the rainbow. However the observer normally sees only an arc formed by illuminated droplets above the ground and centered on a line from the sun to the observer. This happens because light travels at different speeds in different mediums. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist. To understand why light bends imagine you re pushing a shopping cart across a parking lot. Rainbows caused by sunlight always appear in the section of sky directly opposite the sun. A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
A rainbow is formed when light generally sunlight passes through water droplets hanging in the atmosphere. This dispersion of light allows us to see the spectrum of colors that form a rainbow 2. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. Refraction is also responsible for rainbows and for the splitting of white light into a rainbow spectrum as it passes through a glass prism glass has a higher refractive index than air. This second reflection causes the colours on the secondary rainbow to be reversed.
 Source: weathernationtv.com
Source: weathernationtv.com
The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. A rainbow is formed when light generally sunlight passes through water droplets hanging in the atmosphere. Red is at the top for the primary rainbow but in the secondary rainbow red is at the bottom. The light waves change direction as they pass through the water droplets resulting in two processes. To view a rainbow your back must be to the sun as you look at an approximately 40 degree angle above the ground into a region of the atmosphere with suspended droplets of water or even a light mist.
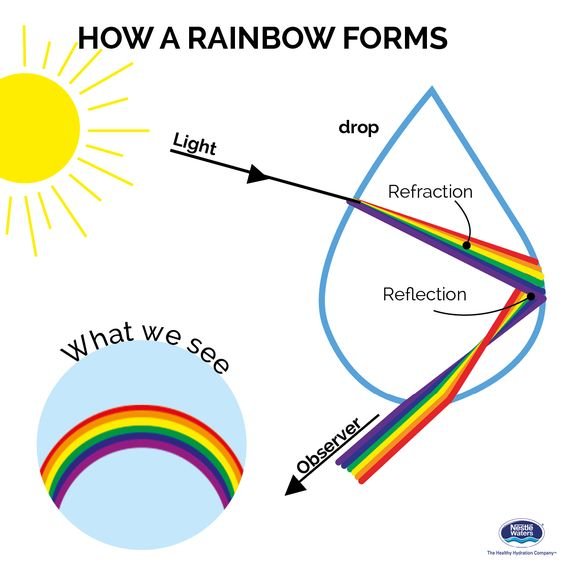 Source: steemit.com
Source: steemit.com
Light enters a drop of water and is reflected from the back of the drop as shown in figure 4. Red is at the top for the primary rainbow but in the secondary rainbow red is at the bottom. A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day. The light is refracted both as it enters and as it leaves the drop. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves.
 Source: webexhibits.org
Source: webexhibits.org
Red is at the top for the primary rainbow but in the secondary rainbow red is at the bottom. Refraction is also responsible for rainbows and for the splitting of white light into a rainbow spectrum as it passes through a glass prism glass has a higher refractive index than air. A rainbow is an excellent demonstration of the dispersion of light and one more piece of evidence that visible light is composed of a spectrum of wavelengths each associated with a distinct color. In nature a rainbow is formed when sunlight is refracted on entering a droplet of water reflected inside the back of the droplet and finally refracted again on leaving the droplet. Light bends or more accurately changes directions when it travels from one medium to another.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This happens because light travels at different speeds in different mediums. The light waves change direction as they pass through the water droplets resulting in two processes. The formation of a rainbow involves physical phenomenon which includes dispersion refraction reflection and total internal reflection. This concentration of light rays is the rainbow that we see. The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The secondary rainbow that can sometimes be seen is caused by each ray of light reflecting twice on the inside of each droplet before it leaves. The light is refracted both as it enters and as it leaves the drop. When a beam of white light passes from air into a material having an index of refraction that varies with frequency a phenomenon known as dispersion occurs in which different coloured components. However the observer normally sees only an arc formed by illuminated droplets above the ground and centered on a line from the sun to the observer. A rainbow occurs as a result of the interaction between sunlight water and air and this is the reason why it is mostly visible when there is a sunny rainy day.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title light refraction rainbow by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
