Movement of paramecium
Home » Science Education » Movement of parameciumMovement of paramecium
Movement Of Paramecium. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction. To obtain food the paramecium uses its cilia to make movement that helps to sweep the prey through the oral groove and into the cell. Cilia are arranged all around the cell and have a two phase movement.
 Paramecium General Characters Locomotion And Nutrition Study Score From studyandscore.com
Paramecium General Characters Locomotion And Nutrition Study Score From studyandscore.com
The beat of each cilium has two phases. The first is an effective stoke where the cilium is relatively stiff and the recovery stroke where cilium curls loosely and then sweeps forward. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction. They rotate the cilia around its own axis to move forward it also helps them to push the food into the gullet. The food passes from the oral groove into the gullet from where the particles enter the cytostome. Cilia are arranged all around the cell and have a two phase movement.
Unlike us that only have two arms a paramecium cell has thousands of cilia.
The cilia on a paramecium move in two directions. They rotate the cilia around its own axis to move forward it also helps them to push the food into the gullet. The movement of cilia can be divided into effective forward and recovery backward stroke. Paramecium is a unicellular organism with a shape resembling the sole of a shoe. The first is an effective stoke where the cilium is relatively stiff and the recovery stroke where cilium curls loosely and then sweeps forward. Movement of paramecium cells is caused by the control of calcium ions inside the cell and membrane potentials.
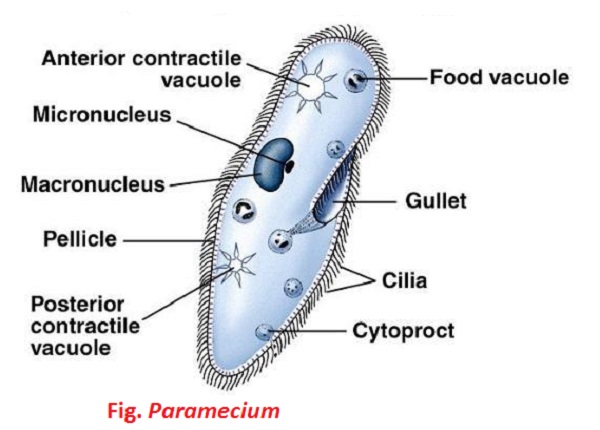 Source: microbiologynotes.com
Source: microbiologynotes.com
Paramecium is mostly heterotrophic and thus a consumer that feed on microorganisms such as bacteria algae and yeasts for their nutrition. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. The simplest explanation for the avoidance reaction is that membrane potential controls the influx of calcium ions which regulates the beat frequency and angles of cilia on the surface of the cell. Paramecium is a unicellular organism with a shape resembling the sole of a shoe. Unlike us that only have two arms a paramecium cell has thousands of cilia.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. However it is capable of changing its direction when it comes in contact with a solid object or a predator. Movement a paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. The movement of cilia can be divided into effective forward and recovery backward stroke. It ranges from 50 to 300um in size which varies from species to species.
 Source: onlyzoology.com
Source: onlyzoology.com
The first is an effective stoke where the cilium is relatively stiff and the recovery stroke where cilium curls loosely and then sweeps forward. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. The speed of the movement is 4 times of its body s length per second. The beat of each cilium has two phases. The creatures move forwards by beating their cilia at a backward angle to thrust themselves through the water.
 Source: emedicalprep.com
Source: emedicalprep.com
The paramecium moves using its cilia. The paramecium moves using its cilia. The beat of each cilium has two phases. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water. The first is an effective stoke where the cilium is relatively stiff and the recovery stroke where cilium curls loosely and then sweeps forward.
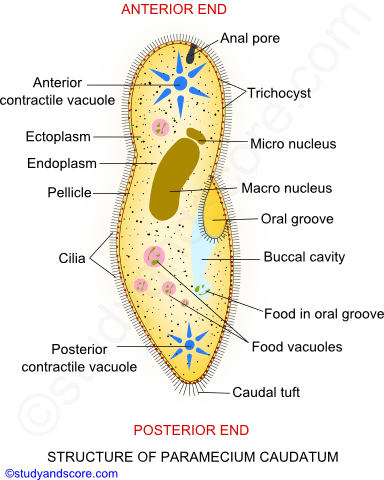 Source: studyandscore.com
Source: studyandscore.com
Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water. A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. In this figure stroke pattern of cilia on a paramecium. However it is capable of changing its direction when it comes in contact with a solid object or a predator. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction.
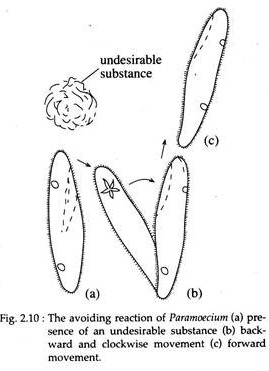 Source: notesonzoology.com
Source: notesonzoology.com
A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. To obtain food the paramecium uses its cilia to make movement that helps to sweep the prey through the oral groove and into the cell. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction. A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion.
 Source: microbiologynote.com
Source: microbiologynote.com
A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. The speed of the movement is 4 times of its body s length per second. Movement a paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. It is mostly found in a freshwater environment. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water.
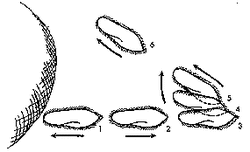 Source: parameciuminfo.weebly.com
Source: parameciuminfo.weebly.com
Paramecium is mostly heterotrophic and thus a consumer that feed on microorganisms such as bacteria algae and yeasts for their nutrition. Unlike us that only have two arms a paramecium cell has thousands of cilia. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
It propels itself by a coordinated whipping movement by the cilia. To back up they beat forwards. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction. It is a single celled eukaryote belonging to kingdom protista and is a well known genus of ciliate protozoa. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth.
 Source: studyandscore.com
Source: studyandscore.com
A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. The beat of each cilium has two phases. It ranges from 50 to 300um in size which varies from species to species. The cilia on a paramecium move in two directions.
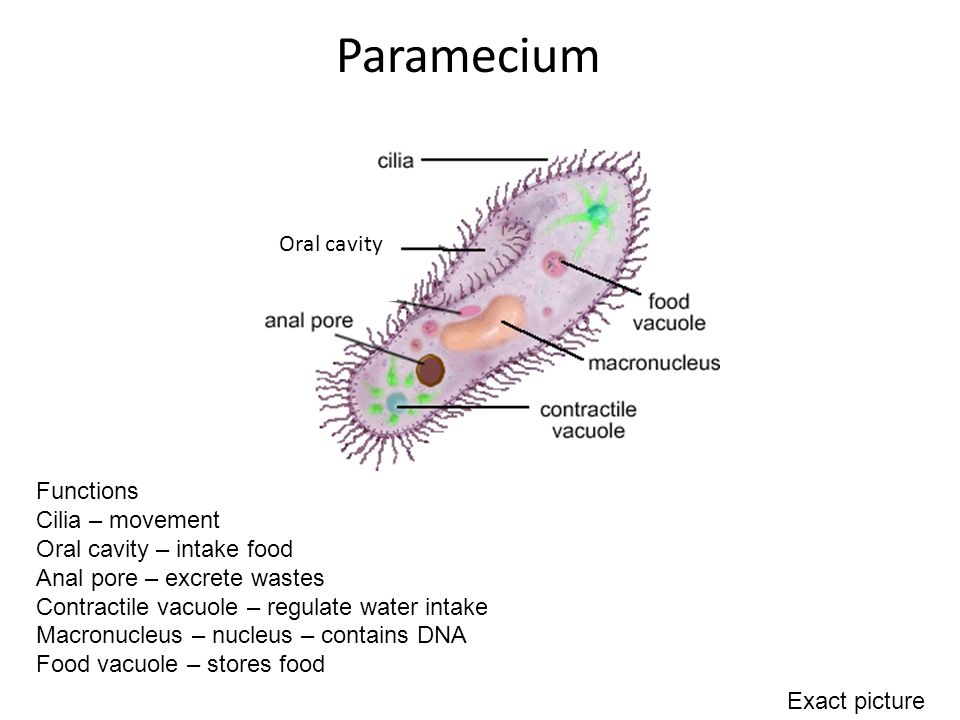 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
It propels itself by a coordinated whipping movement by the cilia. The simplest explanation for the avoidance reaction is that membrane potential controls the influx of calcium ions which regulates the beat frequency and angles of cilia on the surface of the cell. Cilia are arranged all around the cell and have a two phase movement. To obtain food the paramecium uses its cilia to make movement that helps to sweep the prey through the oral groove and into the cell. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water.
![]() Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth. Unlike us that only have two arms a paramecium cell has thousands of cilia. To obtain food the paramecium uses its cilia to make movement that helps to sweep the prey through the oral groove and into the cell. Movement a paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body. Paramecium is mostly heterotrophic and thus a consumer that feed on microorganisms such as bacteria algae and yeasts for their nutrition.
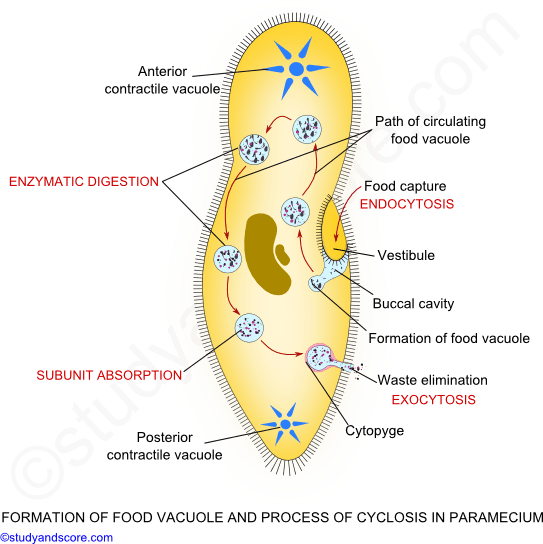 Source: studyandscore.com
Source: studyandscore.com
To obtain food the paramecium uses its cilia to make movement that helps to sweep the prey through the oral groove and into the cell. However it is capable of changing its direction when it comes in contact with a solid object or a predator. Cilia are arranged all around the cell and have a two phase movement. Paramecium can move in reverse by rotating the cilia in reverse direction. Movement a paramecium propels itself by whiplash movements of the cilia which are arranged in tightly spaced rows around the outside of the body.

The simplest explanation for the avoidance reaction is that membrane potential controls the influx of calcium ions which regulates the beat frequency and angles of cilia on the surface of the cell. It is mostly found in a freshwater environment. Paramecium is a unicellular organism with a shape resembling the sole of a shoe. Paramecium generally thrusts itself forward traveling in a straight line through the water. They also spin as they swim through the water allowing them to collect food which is pushed by the cilia into the mouth.
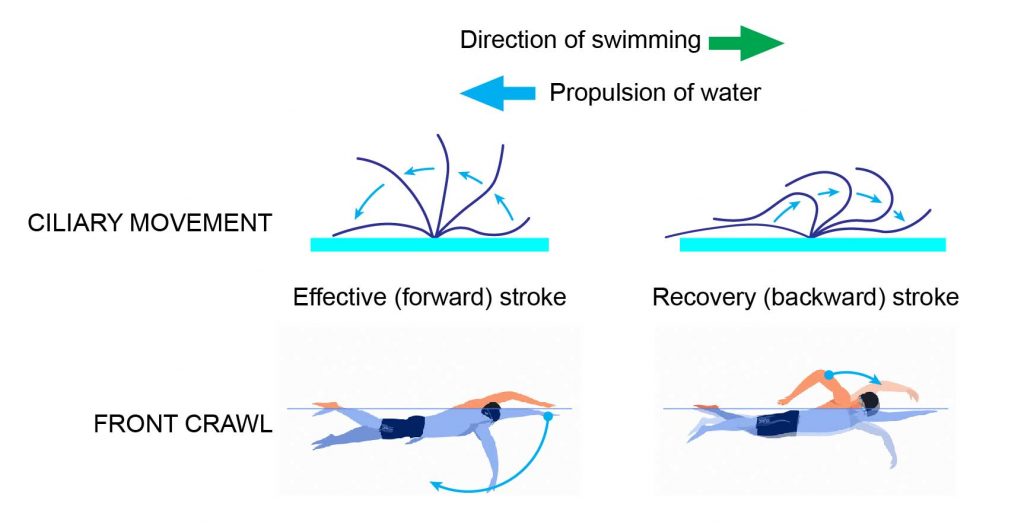 Source: rsscience.com
Source: rsscience.com
It ranges from 50 to 300um in size which varies from species to species. A fast effective stroke during which the cilium is relatively stiff followed by a slow recovery stroke during which the cilium curls loosely to one side and sweeps forward in a counter clockwise fashion. However it is capable of changing its direction when it comes in contact with a solid object or a predator. The paramecium moves using its cilia. Cilia are arranged all around the cell and have a two phase movement.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title movement of paramecium by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
