Sensory nerves of the skin
Home » Science Education » Sensory nerves of the skinSensory nerves of the skin
Sensory Nerves Of The Skin. A minimally invasive 3 mm punch biopsy not requiring sutures is usually taken from a distal skin site with minimal sensory abnormalities fixed cut into thick sections and stained immunohistochemically. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. A large portion of the human sensory cortex receives sensory messages from the skin of the face and the hands areas that are especially well supplied with receptor organs.
 Sensory Receptors In The Skin Pressure Vibration Temperature Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image 124765561 From 123rf.com
Sensory Receptors In The Skin Pressure Vibration Temperature Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image 124765561 From 123rf.com
It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. Skin biopsy the mainstay of the dermatologist has become a valuable tool for neurologists to diagnose disorders that involve unmyelinated sensory nerves. Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve. Nerve fibers innervating the skin originate from dorsal root ganglia nerve cell bodies of sensory nerves hsieh et al 1997. Sensory nerves originate from a number of places for example sensory nerves to the skin covering the neck and posterior scalp come from the cervical nerves. When these nerves are not functioning properly they can produce sensations such as numbness pins and needles pain tingling or burning.
The sensory fibers and their specialized corpuscular end organs are receptors for touch pain temperature itch and physical and chemical stimuli.
Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve. Sensory nerves found in the epidermis mediate touch reception pain and thermal sensation. Skin biopsy the mainstay of the dermatologist has become a valuable tool for neurologists to diagnose disorders that involve unmyelinated sensory nerves. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations. When these nerves are not functioning properly they can produce sensations such as numbness pins and needles pain tingling or burning.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
The skin is innervated by two types of nerve fibers sensory and autonomic. Sensory nerves originate from a number of places for example sensory nerves to the skin covering the neck and posterior scalp come from the cervical nerves. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. A large portion of the human sensory cortex receives sensory messages from the skin of the face and the hands areas that are especially well supplied with receptor organs. However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve.
 Source: 123rf.com
Source: 123rf.com
The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek. Sensory nerves originate from a number of places for example sensory nerves to the skin covering the neck and posterior scalp come from the cervical nerves. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek. These nerves are the subject of evaluation when examining a skin biopsy after it has been immunostained. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations.
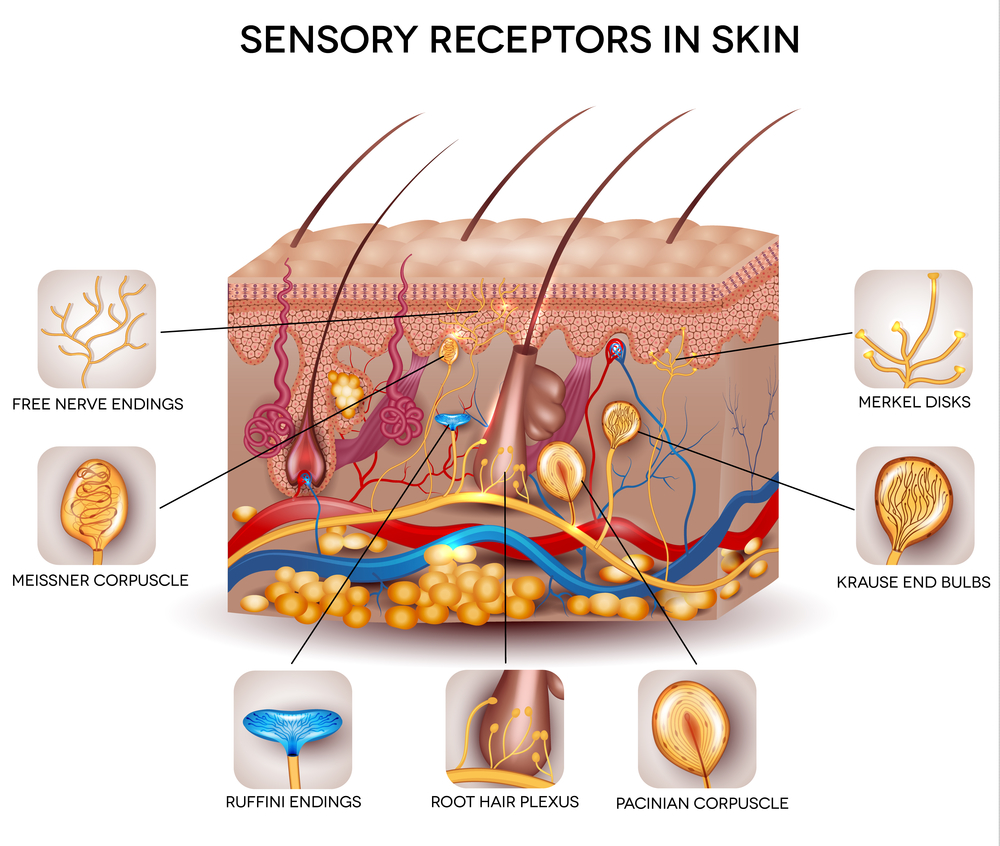 Source: integrativelearningcenter.org
Source: integrativelearningcenter.org
The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. The skin is innervated by two types of nerve fibers sensory and autonomic. A minimally invasive 3 mm punch biopsy not requiring sutures is usually taken from a distal skin site with minimal sensory abnormalities fixed cut into thick sections and stained immunohistochemically. Skin biopsy the mainstay of the dermatologist has become a valuable tool for neurologists to diagnose disorders that involve unmyelinated sensory nerves.
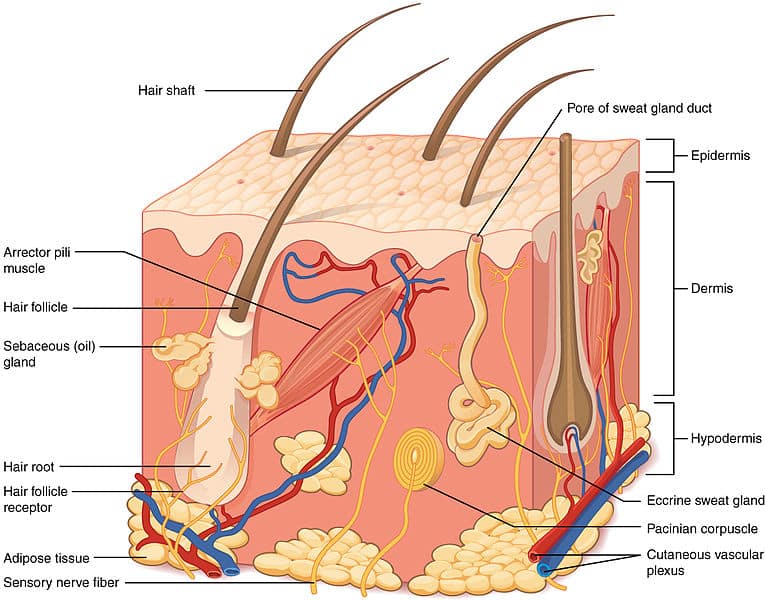 Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Source: teachmeanatomy.info
Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor. Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor. The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek.
 Source: neurones.co.uk
Source: neurones.co.uk
However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations. Skin biopsy the mainstay of the dermatologist has become a valuable tool for neurologists to diagnose disorders that involve unmyelinated sensory nerves. Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor.
 Source: neuronexperts.com
Source: neuronexperts.com
However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. In some cases the dermatome is less specific and in other cases it is more specific modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves but there are minor variations in some of the details. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek. Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. A large portion of the human sensory cortex receives sensory messages from the skin of the face and the hands areas that are especially well supplied with receptor organs. The borders designated by the diagrams in the 1918 edition of gray s anato. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations. In some cases the dermatome is less specific and in other cases it is more specific modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves but there are minor variations in some of the details.
 Source: vetmed.wisc.edu
Source: vetmed.wisc.edu
When these nerves are not functioning properly they can produce sensations such as numbness pins and needles pain tingling or burning. The skin is innervated by two types of nerve fibers sensory and autonomic. The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. In some cases the dermatome is less specific and in other cases it is more specific modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves but there are minor variations in some of the details. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek.
 Source: hopkinsmedicine.org
Source: hopkinsmedicine.org
However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. In some cases the dermatome is less specific and in other cases it is more specific modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves but there are minor variations in some of the details. The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v. Sensory nerves originate from a number of places for example sensory nerves to the skin covering the neck and posterior scalp come from the cervical nerves. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek.
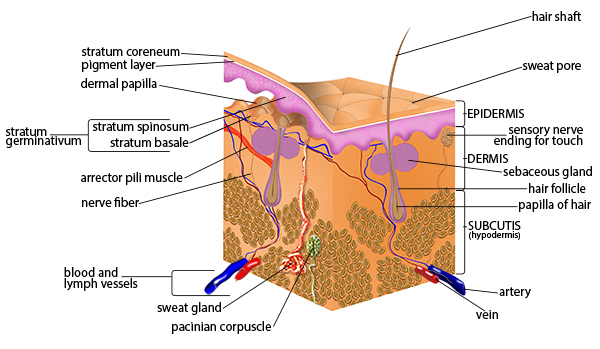 Source: training.seer.cancer.gov
Source: training.seer.cancer.gov
Sensory nerves originate from a number of places for example sensory nerves to the skin covering the neck and posterior scalp come from the cervical nerves. The skin is innervated by two types of nerve fibers sensory and autonomic. A large portion of the human sensory cortex receives sensory messages from the skin of the face and the hands areas that are especially well supplied with receptor organs. Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor. It is the only cranial nerve supplying sensory information to the brain from the skin of the face.
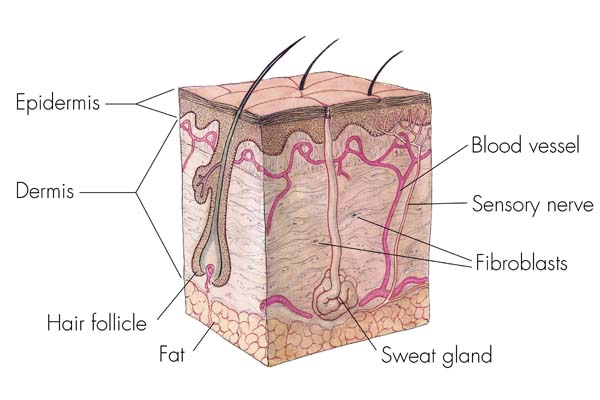 Source: livescience.com
Source: livescience.com
The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations. Sensory nerves found in the epidermis mediate touch reception pain and thermal sensation. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. These nerves are the subject of evaluation when examining a skin biopsy after it has been immunostained. However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve.

Nerve fibers innervating the skin originate from dorsal root ganglia nerve cell bodies of sensory nerves hsieh et al 1997. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. In some cases the dermatome is less specific and in other cases it is more specific modern texts are in agreement about which areas of the skin are served by which nerves but there are minor variations in some of the details. However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. Nerve fibers innervating the skin originate from dorsal root ganglia nerve cell bodies of sensory nerves hsieh et al 1997.
 Source: mediastorehouse.com
Source: mediastorehouse.com
Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor. Sensory nerves found in the epidermis mediate touch reception pain and thermal sensation. A minimally invasive 3 mm punch biopsy not requiring sutures is usually taken from a distal skin site with minimal sensory abnormalities fixed cut into thick sections and stained immunohistochemically. However a dermatome only specifies the area served by a spinal nerve. The sensory nerves in the epidermis serve to sense and transmit heat pain and other noxious sensations.
 Source: idaakasmidar.blogspot.com
Source: idaakasmidar.blogspot.com
The borders designated by the diagrams in the 1918 edition of gray s anato. The sensory fibers and their specialized corpuscular end organs are receptors for touch pain temperature itch and physical and chemical stimuli. It is important to distinguish this nerve from the buccal branch of the facial nerve which functions to provide motor innervation to the buccinator muscle on the cheek. Cutaneous innervation refers to the area of the skin which is supplied by a specific cutaneous nerve. The muscles of mastication the ones that move your mouth and jaw when you eat are innervated by the mandibular nerve motor fibers of cn v.
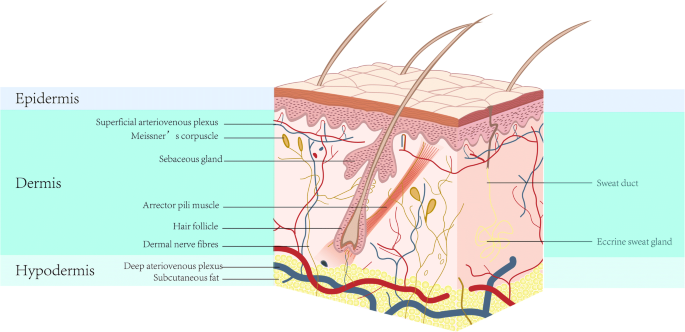 Source: translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com
Source: translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com
Sensory information from the skin over the rest of the body is carried to the cns by spinal nerves injections of anesthetic by a dentist are designed to block sensory transmission through branches of the trigeminal nerve from the teeth these dental branches of the trigeminal nerve are probably anesthetized more often than any other nerves in the body the oculomotor nerve iii is somatic motor. It is the only cranial nerve supplying sensory information to the brain from the skin of the face. Sensory nerves found in the epidermis mediate touch reception pain and thermal sensation. The buccal nerve is another branch of the mandibular nerve and is responsible for supplying sensory innervation to the skin over the buccal membrane internal surface of the cheek. A minimally invasive 3 mm punch biopsy not requiring sutures is usually taken from a distal skin site with minimal sensory abnormalities fixed cut into thick sections and stained immunohistochemically.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title sensory nerves of the skin by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
