The science behind rainbows
Home » Science Education » The science behind rainbowsThe science behind rainbows
The Science Behind Rainbows. Read on to discover the science behind rainbows. The correct angle between the sunlight the water droplets and the observer s eyes. A single rainbow is an optical illusion created by the reflection refraction and dispersion of light through the prism of a water drop. This is meant to represent the vitality of the queer community.
 The Science Behind Moonbows Or Rainbows Seen At Night The Weather Channel Articles From The Weather Channel Weather Com From weather.com
The Science Behind Moonbows Or Rainbows Seen At Night The Weather Channel Articles From The Weather Channel Weather Com From weather.com
A single rainbow is an optical illusion created by the reflection refraction and dispersion of light through the prism of a water drop. Read on to discover the science behind rainbows. The sun or other source of light is usually behind the person seeing the rainbow. Rainbows are the result of the refraction and reflection of light. A rainbow has three requirements. In this article we ll find out how rain and the sun align to put color in the sky.
Keeping with the spirit of pride month i bring you the science behind rainbows the symbol chosen for the lgbtq community for its happy positive image.
When sunlight emerges through the clouds following a rainstorm that light hits the water drops that are still. In fact the center of a primary rainbow is the antisolar point the imaginary point exactly opposite the sun. It s a good bet that most of the artists behind these tales were totally mystified by the rainbow phenomenon just like most people are today. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. It catches our eye signifies the calm after the storm and can lead us to the pot of gold according to an old legend. As we know that the sunlight coming from the sun is mixture of many colours of light and each colour of light having different wavelength and frequency.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
W hat is the science reason behind rainbow formation. Keeping with the spirit of pride month i bring you the science behind rainbows the symbol chosen for the lgbtq community for its happy positive image. Rainbows are the result of the refraction and reflection of light. However due to most people viewing a rainbow on the ground we only see a semi circle or arc of the rainbow. A rainbow is in fact a full circle of light.
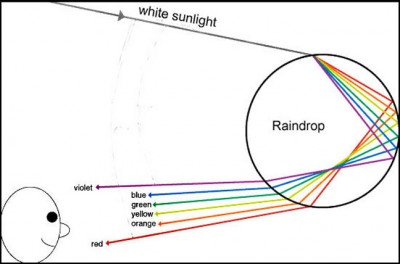 Source: inters.org
Source: inters.org
A single rainbow is an optical illusion created by the reflection refraction and dispersion of light through the prism of a water drop. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Rainbows can be full circles. It s just basic optics. But the science of rainbows is really very simple.
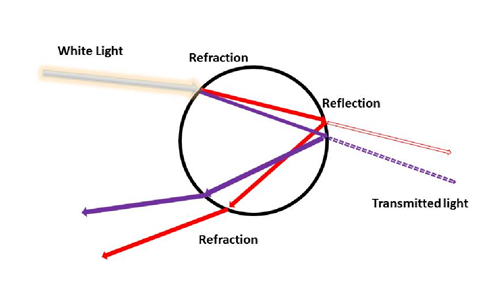 Source: carolina.com
Source: carolina.com
The sun or other source of light is usually behind the person seeing the rainbow. The correct angle between the sunlight the water droplets and the observer s eyes. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. Rainbows can be full circles. It was created to replace the darkness of the pink triangle which was previously the most prominent gay.
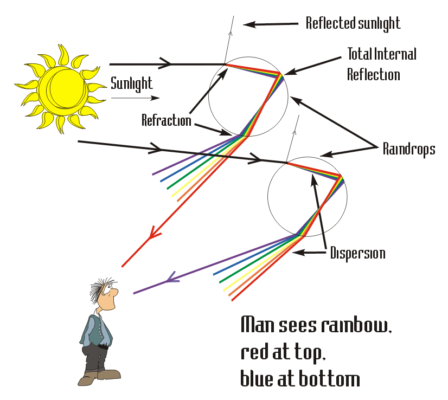 Source: learningliftoff.com
Source: learningliftoff.com
Rainbows are created by both reflection and refraction bending of light in water droplets in the atmosphere which results in a spectrum of light appearing. It s just basic optics. In this article we ll find out how rain and the sun align to put color in the sky. As we know that the sunlight coming from the sun is mixture of many colours of light and each colour of light having different wavelength and frequency. The correct angle between the sunlight the water droplets and the observer s eyes.
 Source: learningliftoff.com
Source: learningliftoff.com
However due to most people viewing a rainbow on the ground we only see a semi circle or arc of the rainbow. Rainbows are the result of the refraction and reflection of light. It was created to replace the darkness of the pink triangle which was previously the most prominent gay. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. Before we explain the science of double rainbows let s review the science behind a single rainbow.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It s just basic optics. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. As we know that the sunlight coming from the sun is mixture of many colours of light and each colour of light having different wavelength and frequency. Keeping with the spirit of pride month i bring you the science behind rainbows the symbol chosen for the lgbtq community for its happy positive image. The correct angle between the sunlight the water droplets and the observer s eyes.
 Source: eo.ucar.edu
Source: eo.ucar.edu
However due to most people viewing a rainbow on the ground we only see a semi circle or arc of the rainbow. The sun or other source of light is usually behind the person seeing the rainbow. It was created to replace the darkness of the pink triangle which was previously the most prominent gay. It s just basic optics. W hat is the science reason behind rainbow formation.
 Source: rainbowsymphonystore.com
Source: rainbowsymphonystore.com
When sunlight emerges through the clouds following a rainstorm that light hits the water drops that are still. A rainbow is in fact a full circle of light. This is meant to represent the vitality of the queer community. Read on to discover the science behind rainbows. It s a good bet that most of the artists behind these tales were totally mystified by the rainbow phenomenon just like most people are today.
 Source: eo.ucar.edu
Source: eo.ucar.edu
When sunlight emerges through the clouds following a rainstorm that light hits the water drops that are still. A rainbow is a meteorological phenomenon that is caused by reflection refraction and dispersion of light in water droplets resulting in a spectrum of light appearing in the sky. However due to most people viewing a rainbow on the ground we only see a semi circle or arc of the rainbow. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. A single rainbow is an optical illusion created by the reflection refraction and dispersion of light through the prism of a water drop.
 Source: rookieparenting.com
Source: rookieparenting.com
However due to most people viewing a rainbow on the ground we only see a semi circle or arc of the rainbow. The correct angle between the sunlight the water droplets and the observer s eyes. It was created to replace the darkness of the pink triangle which was previously the most prominent gay. This is meant to represent the vitality of the queer community. Rainbows can be full circles.
 Source: weather.com
Source: weather.com
It was created to replace the darkness of the pink triangle which was previously the most prominent gay. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. W hat is the science reason behind rainbow formation. Rainbows are the result of the refraction and reflection of light. The sun or other source of light is usually behind the person seeing the rainbow.
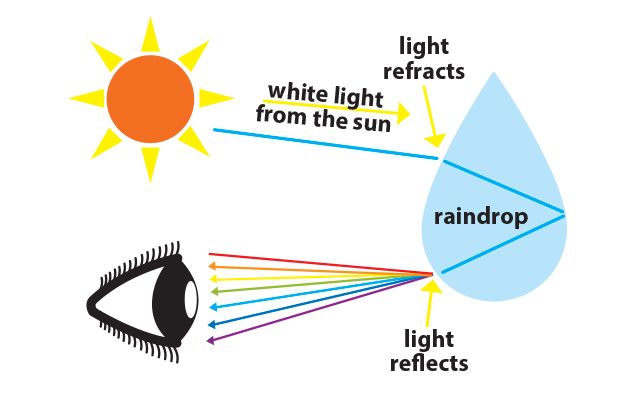 Source: drkarl.com
Source: drkarl.com
Rainbows are created by both reflection and refraction bending of light in water droplets in the atmosphere which results in a spectrum of light appearing. It takes the form of a multicoloured circular arc. Before we explain the science of double rainbows let s review the science behind a single rainbow. A rainbow has three requirements. It catches our eye signifies the calm after the storm and can lead us to the pot of gold according to an old legend.
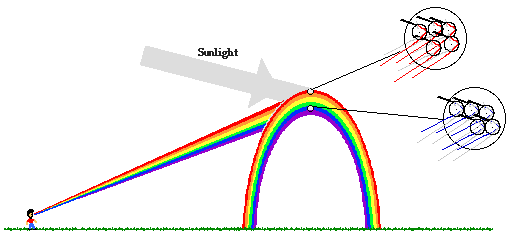 Source: physicsclassroom.com
Source: physicsclassroom.com
Keeping with the spirit of pride month i bring you the science behind rainbows the symbol chosen for the lgbtq community for its happy positive image. It s just basic optics. As we know that the sunlight coming from the sun is mixture of many colours of light and each colour of light having different wavelength and frequency. Rainbows are the result of the refraction and reflection of light. But the science of rainbows is really very simple.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
But the science of rainbows is really very simple. The wavelength is decreases when we move from red to violet and frequency increases. In fact the center of a primary rainbow is the antisolar point the imaginary point exactly opposite the sun. Before we explain the science of double rainbows let s review the science behind a single rainbow. Keeping with the spirit of pride month i bring you the science behind rainbows the symbol chosen for the lgbtq community for its happy positive image.
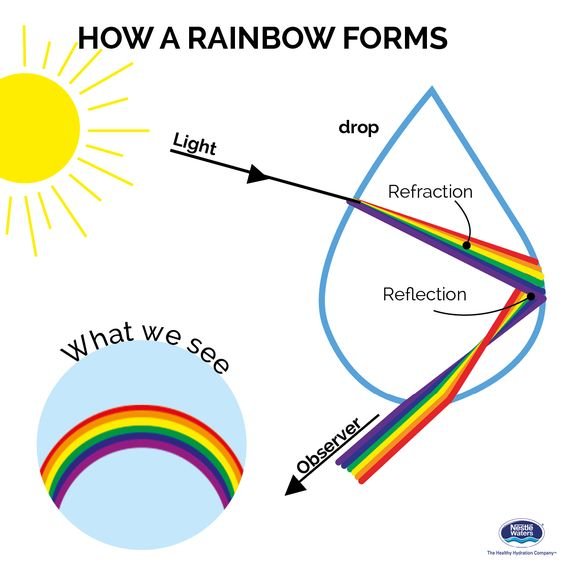 Source: steemit.com
Source: steemit.com
A rainbow is in fact a full circle of light. But the science of rainbows is really very simple. As we know that the sunlight coming from the sun is mixture of many colours of light and each colour of light having different wavelength and frequency. In this article we ll find out how rain and the sun align to put color in the sky. Rainbows can be full circles.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title the science behind rainbows by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
