What does the medulla
Home » Science Education » What does the medullaWhat does the medulla
What Does The Medulla. The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem. The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing.
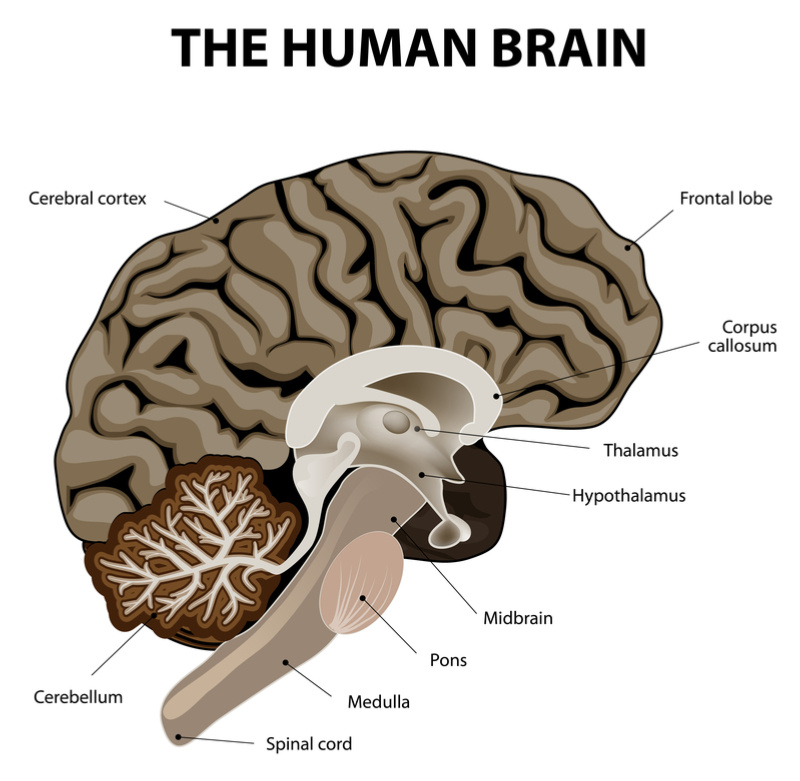 The Medulla Oblongata Get To Know The Most Vital Part Of The Brain Mindvalley Blog From blog.mindvalley.com
The Medulla Oblongata Get To Know The Most Vital Part Of The Brain Mindvalley Blog From blog.mindvalley.com
Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing. The position of the medulla oblongata enables it to be the primary connection of the central nervous system to the peripheral nervous system as it is continuous with the spinal cord. The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. This part of the brain is a center for respiration and circulation.
Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem.
The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. Anatomy of the medulla oblongata. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing. Your medulla oblongata is located at about the same level or slightly above this hole.
 Source: verywellhealth.com
Source: verywellhealth.com
The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing. Both adrenaline and noradrenaline are produced from the amino acid tyrosine through multiple reactions. The medulla oblongata is connected by the pons to the midbrain and is continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord with which it merges at the opening foramen magnum at the base of the skull. Updated november 13 2019. The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing.
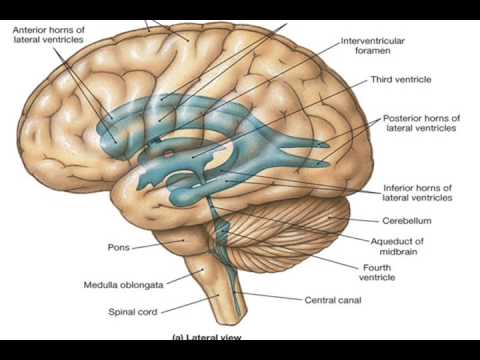 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The medulla oblongata and spinal cord merge at the opening located at the base of the skull the foramen magnum. The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. The medulla oblongata is connected by the pons to the midbrain and is continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord with which it merges at the opening foramen magnum at the base of the skull. The medulla oblongata also known as the medulla directly controls certain ans responses such as heart rate breathing blood vessel dilation digestion sneezing swallowing and vomiting.
 Source: blog.mindvalley.com
Source: blog.mindvalley.com
The medulla oblongata also known as the medulla directly controls certain ans responses such as heart rate breathing blood vessel dilation digestion sneezing swallowing and vomiting. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. Anatomy of the medulla oblongata. The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing. The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing. The medulla oblongata also known as the medulla directly controls certain ans responses such as heart rate breathing blood vessel dilation digestion sneezing swallowing and vomiting. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. Both adrenaline and noradrenaline are produced from the amino acid tyrosine through multiple reactions.
 Source: thoughtco.com
Source: thoughtco.com
The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers. The medulla oblongata is connected by the pons to the midbrain and is continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord with which it merges at the opening foramen magnum at the base of the skull. Updated november 13 2019. The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers. The medulla oblongata is a portion of the hindbrain that controls autonomic functions such as breathing digestion heart and blood vessel function swallowing and sneezing.
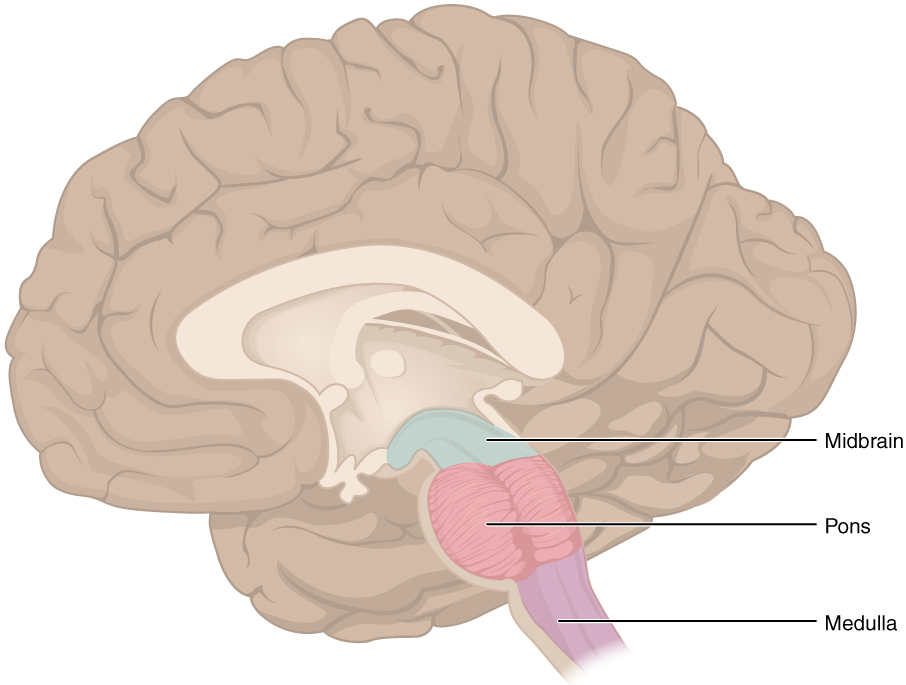 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Updated november 13 2019. The medulla contains the cardiac respiratory vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers. The adrenal medulla is mainly responsible for the synthesis of the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline but also has other secretory functions such as the production of dopamine. The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing.
 Source: ausmed.com
Source: ausmed.com
The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem. The medulla oblongata also known as the medulla directly controls certain ans responses such as heart rate breathing blood vessel dilation digestion sneezing swallowing and vomiting.
 Source: neuroscientificallychallenged.com
Source: neuroscientificallychallenged.com
Your medulla oblongata is located at about the same level or slightly above this hole. The medulla oblongata also known as the medulla directly controls certain ans responses such as heart rate breathing blood vessel dilation digestion sneezing swallowing and vomiting. The adrenal medulla is mainly responsible for the synthesis of the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline but also has other secretory functions such as the production of dopamine. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. The position of the medulla oblongata enables it to be the primary connection of the central nervous system to the peripheral nervous system as it is continuous with the spinal cord.
 Source: healthline.com
Source: healthline.com
The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. The medulla oblongata is connected by the pons to the midbrain and is continuous posteriorly with the spinal cord with which it merges at the opening foramen magnum at the base of the skull. Updated november 13 2019. The adrenal medulla is mainly responsible for the synthesis of the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline but also has other secretory functions such as the production of dopamine.
 Source: brainmadesimple.com
Source: brainmadesimple.com
Updated november 13 2019. Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem. The medulla contains the cardiac respiratory vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. The medulla is comprised of both myelinated white matter and unmyelinated gray matter nerve fibers.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing. The medulla oblongata and spinal cord merge at the opening located at the base of the skull the foramen magnum. This part of the brain is a center for respiration and circulation. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum. The medulla contains the cardiac respiratory vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle. Anatomy of the medulla oblongata. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing.

The medulla contains the cardiac respiratory vomiting and vasomotor centers and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle. The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem. The medulla oblongata helps regulate breathing heart and blood vessel function digestion sneezing and swallowing. Your medulla oblongata is located at about the same level or slightly above this hole.
 Source: verywellhealth.com
Source: verywellhealth.com
Medulla oblongata also called medulla the lowest part of the brain and the lowest portion of the brainstem. Both adrenaline and noradrenaline are produced from the amino acid tyrosine through multiple reactions. The medulla oblongata plays a critical role in transmitting signals between the spinal cord and the higher parts of the brain and in controlling autonomic activities such as heartbeat and. It is a cone shaped neuronal mass responsible for autonomic functions ranging from vomiting to sneezing. Motor and sensory neurons from the midbrain and forebrain travel through the medulla.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what does the medulla by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.
